Volatility Index (VIX): Understanding Market Volatility and Types
2023-09-19 11:11:19
Volatility plays a crucial role in finance by evaluating the risk associated with asset price shifts from stocks to indices. It measures the changes in returns, with high-volatility assets indicating more risk due to unpredictable price changes. For every trader and speculator, a solid grasp of volatility is fundamental. Whether you're trading on the S&P 500 chart or monitoring the Dow Jones Industrial, understanding volatility assists in financial decisions.
Explaining the VIX: A Guide to Market Volatility
The Volatility Index, commonly known as the VIX, is an invaluable tool for traders' keen on understanding market fluctuations. Often dubbed as the "fear index" because it rises during uncertain market conditions, the VIX provides critical insights into market sentiments, allowing traders to tailor their portfolios accordingly.
Initially known as the Chicago Board Options Exchange Volatility Index, the VIX estimates the expected volatility of the U.S. stock market, focusing specifically on the S&P 500 index, over the next 30 days. This prediction is based on the options market, which captures the collective market sentiment.
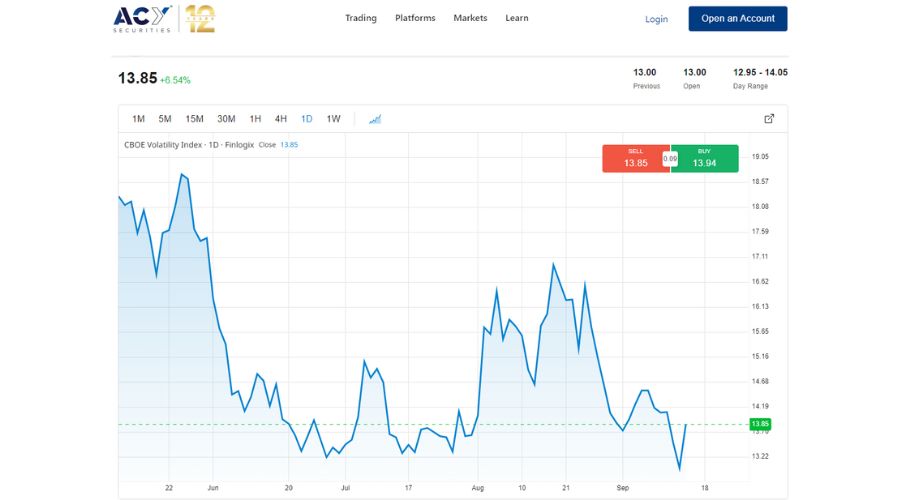
A higher VIX value signals heightened volatility in the S&P 500, symbolizing a surge in market uncertainty. On the flip side, a diminishing VIX suggests an impending phase of market stability, signalling reduced uncertainty. In essence, the VIX serves as a barometer, assisting traders to gauge potential stock price swings and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Types of Volatility
There are various volatility measurements like Standard Deviation, Beta (β), and Implied Volatility. While Standard Deviation gauges price changes over time, Beta determines the volatility of a security compared to the overall market. Implied Volatility, on the other hand, forecasts future price fluctuations based on options prices.
For those looking to open an account with ACY Securities, understanding the intricacies of the VIX can prove pivotal in navigating the ebbs and flows of market volatility.
Measuring Volatility: Two Approaches
Volatility evaluates the magnitude of price changes in an asset. There are two primary methods to assess this metric:
1. Historical Volatility: This method utilizes various statistical tools to determine an asset's past volatility:
- Mean: The average of a set of values. In this context, it refers to the average closing price over a specified period.
- Variance: Measures how spread out the set of values (prices) are from the mean. A high variance indicates that the data points are far from the mean and from each other, indicating more volatility.
- Standard Deviation: The square root of the variance, giving a sense of the average distance between each data point and the mean. In terms of volatility, a higher standard deviation means more price fluctuation.
Using past closing prices within a specific timeframe, this method calculates the standard deviation from the variance. While it quantifies past volatility or risk, its predictive capabilities are limited. For example, considering the closing prices from a 30-day window with prices ranging from $20 to $200 only reflects historical volatility. For a more accurate representation, it is often recommended to study recent data, with the expectation that past trends might continue.
2. Implied Volatility: This method uses option prices to gauge anticipated future volatility. For example, consider a stock (let us call it ABC) trading at $50 per share. If there is a call option for this stock, set to expire in a month with a strike price of $60, the option's price will reflect the market's belief in the stock's likelihood to reach or exceed $60 within that timeframe. Pricing models, like the Black-Scholes model, consider this volatility a significant input. Unlike historical volatility, this method provides a forward-looking perspective on expected price fluctuations.
In summary, while the first approach provides insights based on past data, the second anticipates future changes. Traders, especially those aiming to open an account with ACY Securities, should familiarize themselves with both methods to make informed decisions in a volatile market landscape.
Leveraging the VIX in Shaping Financial Strategies
The Volatility Index (VIX) is a cornerstone for traders and professionals. By providing real-time signals of market movements, the VIX profoundly influences their market decisions. This powerful tool offers a lens to discern potential market uptrends, downtrends, and periods of stability.
The principle of mean reversion, which suggests that asset prices gravitate back to their long-term averages, manifests in the VIX. A surge in the VIX during stable market conditions can be a precursor to price shifts in equities, notably the S&P 500. Conversely, a decline in the VIX often heralds an imminent return to market equanimity.
When the VIX escalates, it acts as an alarm for traders, prompting them to contemplate more secure options like bonds or money market funds. This tactful move safeguards their portfolio amidst market unpredictability. However, as the VIX subsides, opportunities emerge for traders to delve into stocks that, while offering promising returns, might be laden with higher risks.
VIX Thresholds
- 0-15: Symbolizes minimal volatility.
- 15-25: Denotes moderate volatility.
- 25-30: Indicates escalating market turbulence.
- Above 30: Portends pronounced market volatility with potential drastic shifts.
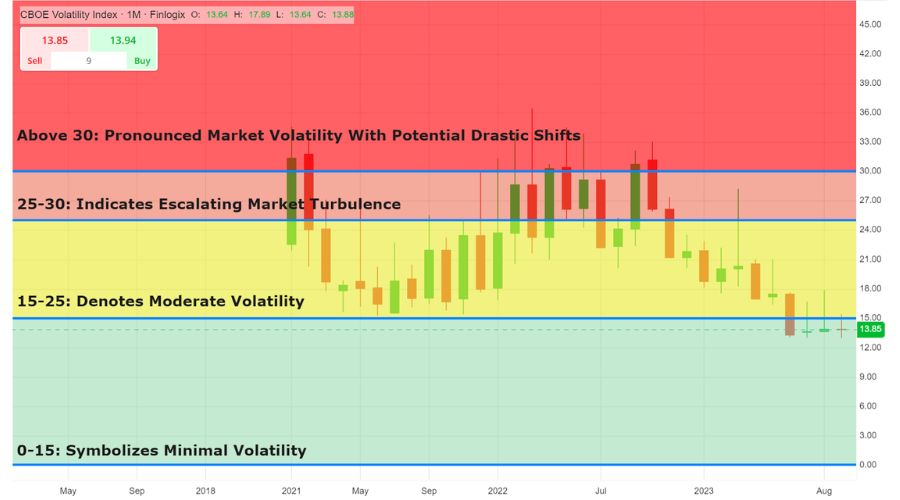
Beyond its function as a gauge, the VIX can be integrated into trading strategies. While it cannot be directly purchased like traditional stocks or bonds, its influence can be leveraged through certain financial instruments:
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): These are funds traded on stock exchanges, similar to stocks. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, and generally tracks an index, allowing traders to get a broad exposure to a particular market or segment without having to buy the individual assets.
- Exchange-Traded Notes (ETNs): ETNs are unsecured debt securities that track an underlying index of securities. Unlike ETFs, ETNs do not actually own the assets in the index they track. Instead, they pay traders the return achieved by the index, minus fees, upon maturity. Because they are debt instruments, they come with the credit risk of the issuer.
Both ETFs and ETNs influenced by the VIX allow traders to capitalize on their movements without having to trade options or futures. These financial instruments are ideal for traders not well-versed with options or futures but still wish to benefit from VIX movements. This dynamic makes the VIX a pivotal component in risk management for traders.
How to trade the VIX index in MT4/MT5
ACY Securities offers a wider range of financial instruments than just forex, including indices like the VIX. Here's how to trade the VIX Index on the MT4 and MT5 platforms:
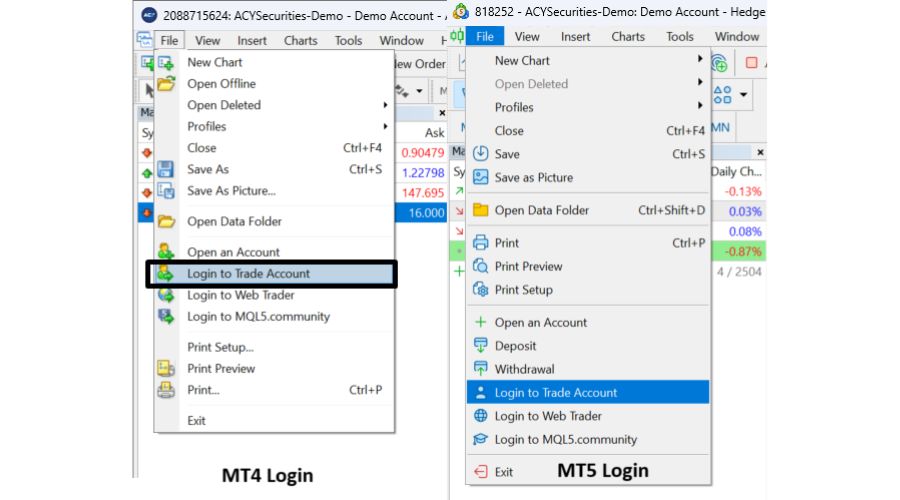
Log into MT4/MT5: Open your MetaTrader platform and enter your account credentials.
Open 'Market Watch': On the left side of the screen, you will find the 'Market Watch' window. If it's not visible, press Ctrl+M to open it.
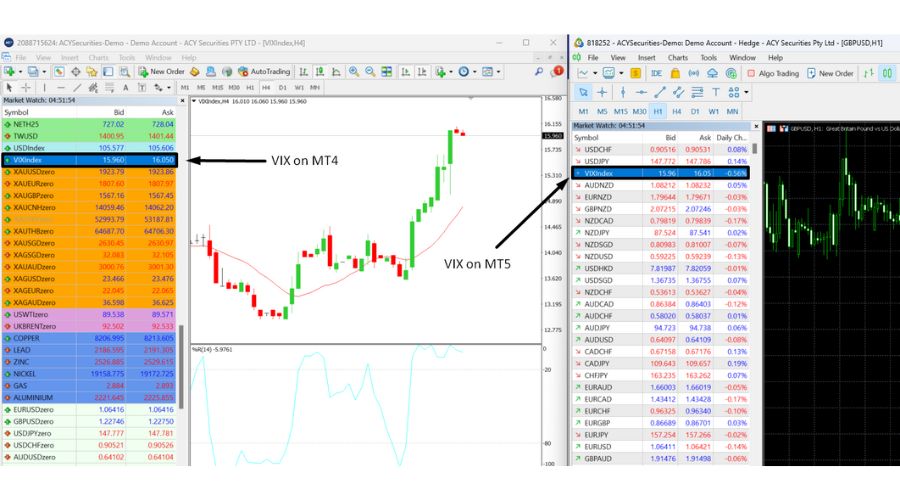
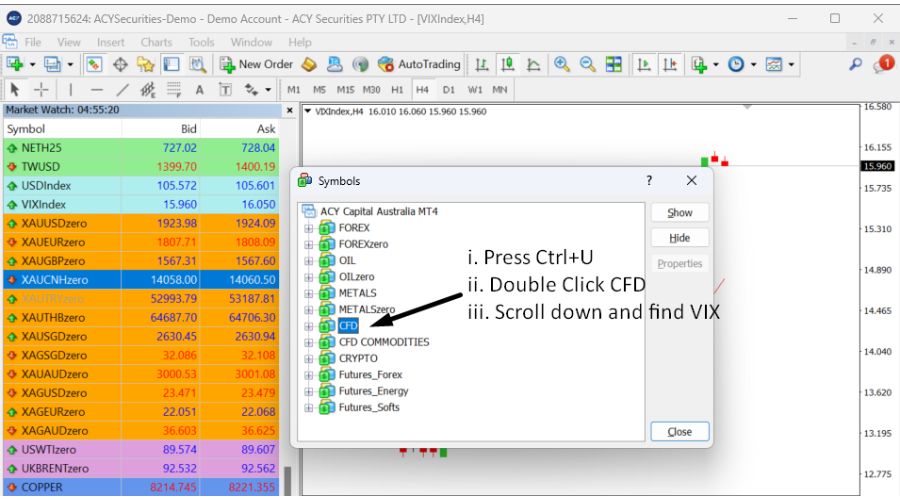
Search for the VIX: There's an easy way to add VIX if it's not viable on your platform. Simply right-click within the 'Market Watch' window.
- Select 'Symbols' or press Ctrl+U.
- A new window will pop up with a list of available instruments.
- Scroll through or search for 'VIX' or a similar name like VIXIndex. Note: The exact name might vary depending on the broker.
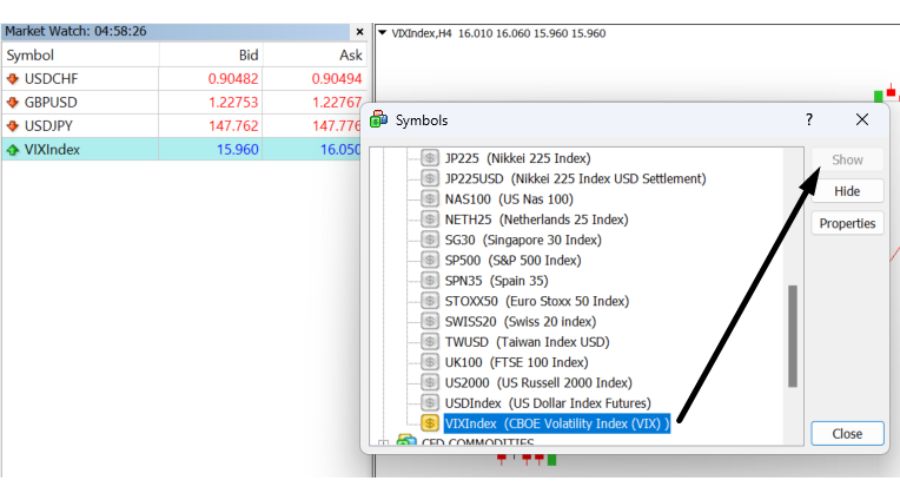
Add VIX to Market Watch:
- Once found, highlight the VIX Index.
- Click on the 'Show Symbol' button.
- The VIX should now be visible in your 'Market Watch' window.
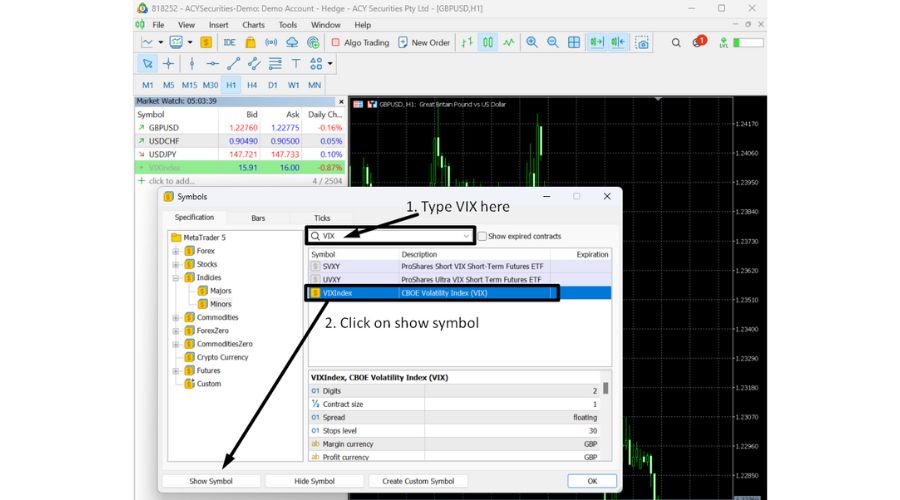
VIX on MetaTrader 5
Discovering the VIX Index on MT5 has become even easier.
- Press Ctrl+U to open the Symbols window.
- Type "VIX" in the search bar.
- Click on 'Show Symbol'.
- The VIX symbol will now be displayed on your MT5 Market Watch.
- Follow the same trading process as in MT4.
Open a New Chart
Drag and drop the VIX Index from the 'Market Watch' window onto the main workspace, or right-click on the VIX and select 'Chart Window'. This will open a new chart for the VIX Index.
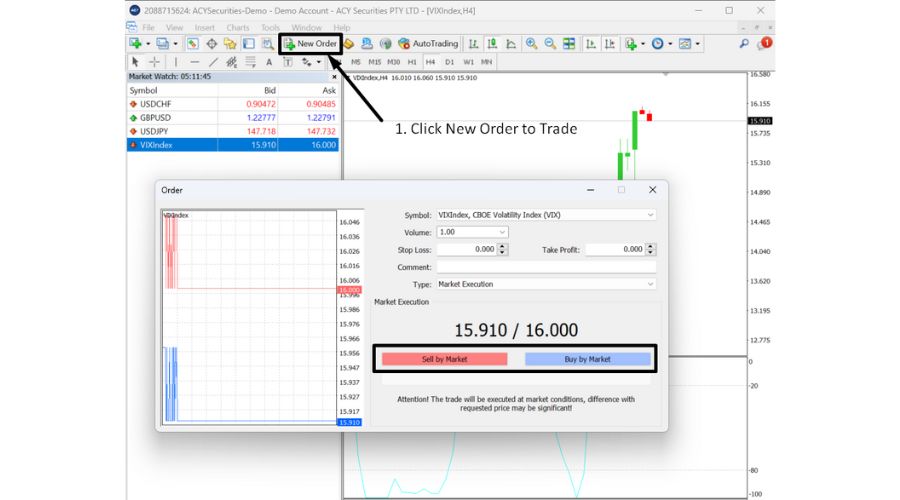
Initiate a Trade
- Right-click on the VIX chart.
- Select 'Trading' and then 'New Order'.
- A trading dialogue box will appear, where you can set your trade parameters, such as lot size, stop loss, and take profit levels.
- Decide whether you anticipate the VIX to rise (Buy) or fall (Sell) and initiate your trade accordingly.
Monitor and Manage Your Trade
- Regularly review your open positions.
- Adjust stop losses and take profit levels as necessary based on market movements and your trading strategy.
Use Technical Analysis Tools
- MT4/MT5 offers a range of tools to help analyze the VIX chart. Utilize indicators, trendlines, and other analysis tools to make informed trading decisions.
Stay Updated
- Always stay informed about major economic events and market news, as these can significantly impact volatility and, by extension, the VIX Index.
- Remember, trading the VIX Index or any other financial instrument comes with risks. Always ensure you have a well-defined strategy and risk management plan in place.
Let's now explore the advantages and disadvantages of index trading.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Index Trading
Index trading, a popular financial strategy, offers several benefits and drawbacks that traders should be aware of. Let us delve deeper into its pros and cons.
Pros:
- Cost-Efficiency: Index trading, especially via Contracts for Difference (CFDs), often leads to significant savings on transaction costs.
- Stability: Indices are a composite of numerous stocks. This diversification means the risk is distributed across multiple assets, leading to fewer drastic value swings, and fostering a more stable trading environment.
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to enter positions without committing the full capital upfront. Instead, they deposit only a portion, or margin, amplifying potential gains. However, this also means that losses can be magnified, necessitating prudent risk management.
Cons:
- Leverage Risk: The double-edged sword of leverage means that while it can amplify gains, it can equally magnify losses. A trader's exposure due to leverage can sometimes surpass their initial deposit, underscoring the critical importance of robust risk management practices.
Index trading combines the allure of cost-saving measures and market stability. However, the inherent risks associated with leverage require traders to approach it with caution and a well-devised risk mitigation strategy.
Conclusion
In volatile financial landscapes, tools like the VIX Index offer a clear perspective on market conditions. While index trading boasts advantages such as cost-efficiency and diversified risk, it is imperative to exercise caution, particularly considering the inherent risks of leverage.
At ACY Securities, we offer valuable educational content and expert-led webinars to help traders navigate the world of CFDs and the forex market. Learn more about Indices, Gold, Oil and other tradable instruments we have on offer at ACY Securities.
You can also explore our MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 trading platforms including access to our free MetaTrader scripts. Then try out your own trading strategies on your own free demo trading account.
Try These Next











