The Truth About Risks in CFD Trading: What you need to know
2024-06-26 14:34:07
CFD trading presents exciting opportunities for significant gains, but it also comes with notable risks. Understanding these risks, including CFD trading risk, is crucial for making informed decisions and creating strategies to minimise financial losses.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key risk factors in CFD trading, such as market volatility, leverage, and liquidity challenges, equipping you with the knowledge needed for safer trading. For more in-depth insights and strategies, check out our resources on risk management and trading strategies at ACY Securities.
Navigating Leverage Risks in CFD Trading
Leverage is a powerful feature in CFD trading, offering the ability to control larger positions than your capital would typically allow, but it is also associated with high risk. While this can amplify your potential gains, it also increases the risks of significant losses. In this guide, we’ll break down leverage, focusing on its basics and real-world implications, tailored for ACY Securities readers.
How Leverage Works
Leverage, or margin, involves borrowing funds from your broker to increase your trading position. This enables traders to access greater market exposure with a smaller initial capital.
For example, imagine John, a beginner trader, wanting to trade in CFDs. He has $1,000 but wishes to trade a position worth $10,000 in the global markets. With a leverage ratio of 1:10, John only needs to deposit $1,000 as margin, while his broker covers the remaining $9,000.
This way, John’s potential gains—and losses—are magnified. It’s essential for traders like John to use leverage cautiously to avoid rapid losses and potentially lose money.
Leverage at ACY Securities
At ACY Securities, we offer diverse trading opportunities across various global markets, including CFDs on forex, commodities, shares, futures, ETFs and indices. Traders benefit from competitive conditions, such as leverage up to 1:500 and tight spreads starting from 0.0 pips for major currency pairs like EUR/USD. This allows traders to maximise their potential in the financial markets, provided they implement strong risk management tools and strategies.
For more detailed information on leveraging CFD trading opportunities and understanding our pricing, visit ACY Securities’ comprehensive trading resources. Leverage your trading potential wisely and make informed decisions with our expert guidance.
Understanding the Risk of Bigger Losses in CFD Trading
Leverage is a double-edged sword in CFD trading, enhancing both potential gains and the risk of substantial losses. This heightened risk arises because traders can control market positions far larger than their initial capital, meaning price movements in the underlying asset can lead to significantly larger losses.
For example: Consider John, who is trading CFDs with an initial capital of $1,000. Without leverage, a 5% decrease in the value of his $10,000 gold trade would result in a $500 loss.
However, with a 1:10 leverage, the same 5% market move would amplify his loss to $5,000, a figure that far exceeds his initial $1,000 capital. This example highlights how leverage can exponentially increase both potential rewards and the risk of losing money rapidly.
Understanding Market Volatility and Its Impact on CFD Trading
Market risk refers to the potential for substantial gains or losses due to fluctuations in exchange rates and the volatility of the market despite careful analysis. Market volatility, a type of market risk, refers to the rate at which asset prices fluctuate over time. High volatility means prices change rapidly, providing opportunities for quick gains or losses. For CFD traders, understanding market volatility is essential, as it can significantly impact your trading outcomes.
For a deeper dive into this topic, check out the video below, where we explore essential strategies like stop-loss orders, portfolio diversification, and staying informed on market trends.
Identifying Volatile Markets
Volatile markets are characterised by rapid price movements. Recognising these markets is vital for CFD traders to adjust their trading strategies effectively.
How to Spot Volatility
Significant and swift changes in asset prices are indicators of volatility. For instance, if a stock's price rises by 10% one day, drops by 15% the next, and then surges by 12%, it indicates a highly volatile market.
Example: Trading CFDs in a Volatile Market
Consider trading CFDs on an energy company’s stock. If the stock’s price experiences sharp fluctuations within short periods, it signals high volatility. For instance, if the stock price jumps 10% in the morning, drops 8% by midday, and then rises another 12% by the close, traders must act swiftly to manage their positions.
Such volatile conditions necessitate a well-thought-out trading strategy to capitalise on gains or minimise losses. Platforms like ACY Securities offer tools and resources to help traders develop effective strategies for managing market volatility and protecting against sudden market movements.
Effective Strategies to Handle Market Volatility in CFD Trading
Navigating the volatile nature of CFD markets can be challenging yet rewarding. Here are some straightforward strategies to manage volatility effectively and make informed trading decisions, tailored for ACY Securities readers.
1. Trading the Trend
One fundamental approach is to identify and follow market trends. Trading in the direction of a consistent market trend can be advantageous. For example, if a stock has been on a downward trend, buying a CFD in anticipation of a rebound might be a viable strategy.
Applying Trend Following with Apple Stocks
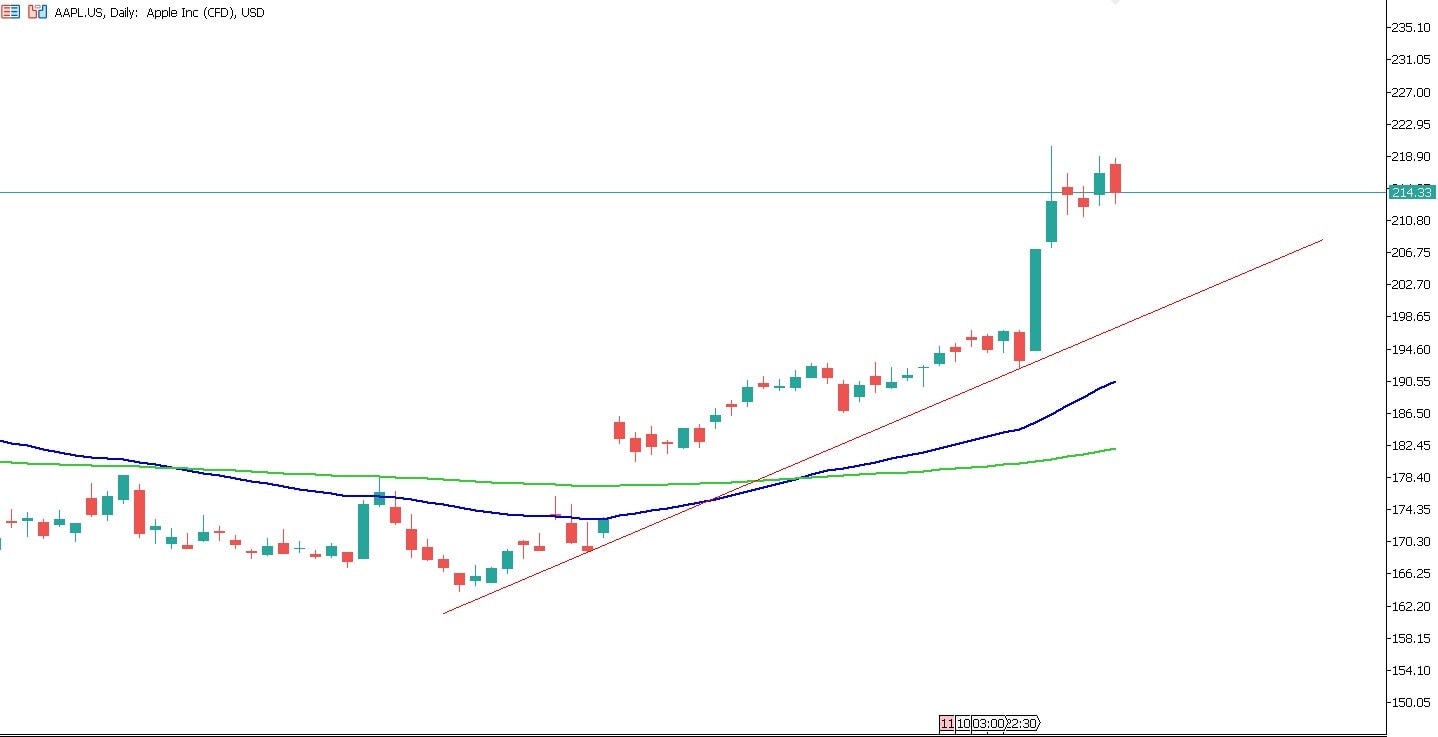
Consider Apple Inc.'s stock chart, which shows a clear upward trendline acting as a support level over time. This trendline indicates a strong uptrend, suggesting potential buying opportunities when the market approaches this line. Historical buying levels at price points such as $178, $182, $190, $198, and $214 align with this upward trendline, indicating potential for yields if the trend continues.
Additionally, the chart shows an EMA (Exponential Moving Average) crossover, where the shorter-term EMA crosses above the longer-term EMA, signalling a bullish trend. This crossover further supports the trend-following strategy, indicating potential buying points during upward market movements.
Risk Management with Stop-Loss Orders
Setting stop-loss orders is crucial to managing risks. This helps limit potential losses if the trend reverses and the stock price fall below the trendline. For instance, if you buy Apple CFDs at $198, setting a stop-loss order at $194 can protect against significant losses if the price drops unexpectedly.
2. Breakout Strategy: Capitalising on Market Momentum
Capitalising on market momentum can be highly effective in CFD trading. Focus on key support (the low-price level that a stock doesn’t typically fall below) and resistance levels (the high price point that a stock struggles to exceed).
Entering a trade when the price breaks these levels can signal a strong move in that direction.
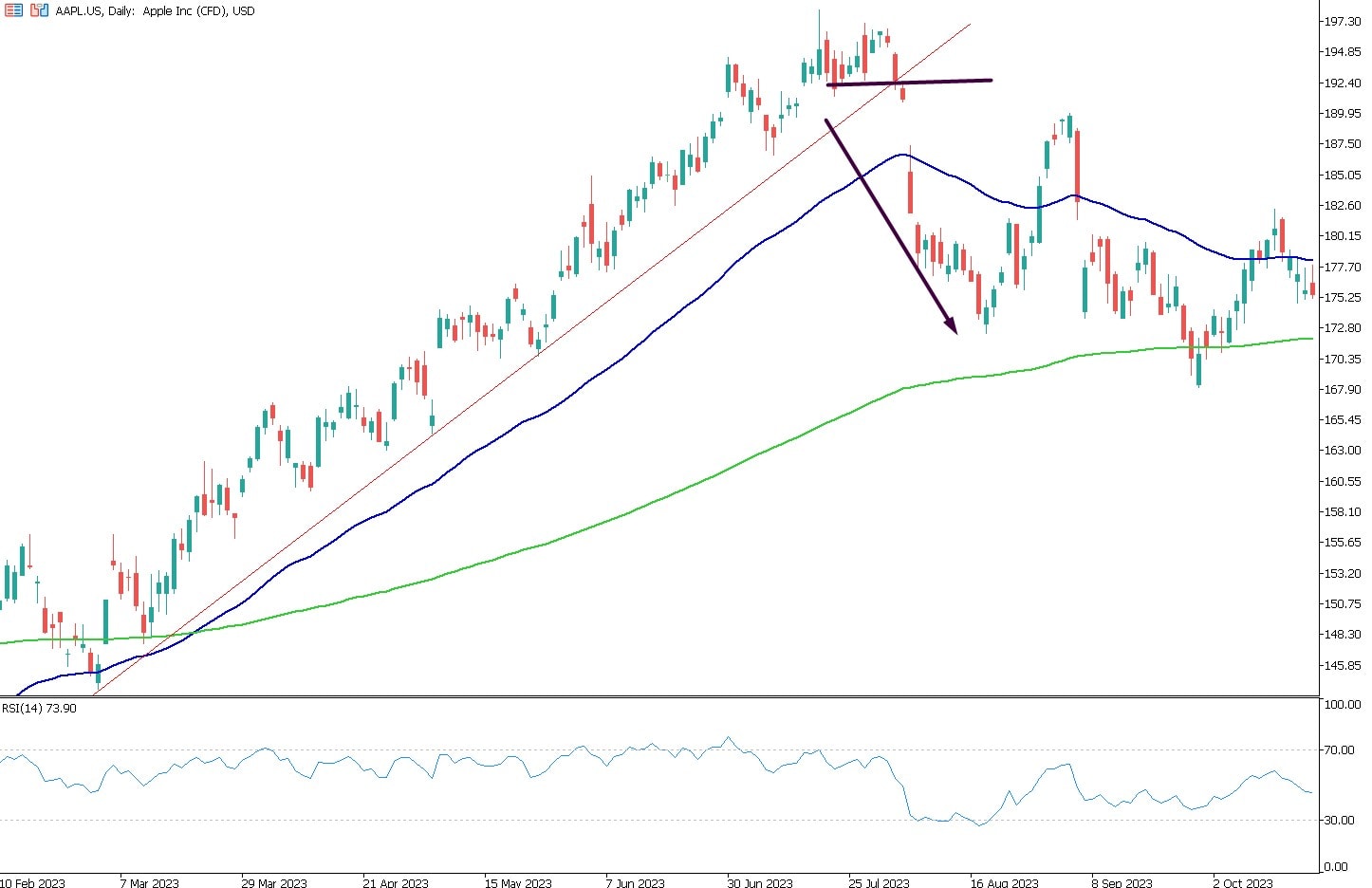
Example: Breakout Strategy with Apple Stocks
In Apple's stock chart, the upward trendline presents two key trading scenarios:
Buying above the trendline when the price action remains supportive.
Selling upon a confirmed breakout below the trendline.
The chart illustrates a situation where Apple's stock price broke through the trendline support at approximately $192. This breakout below the trendline provided a sharp opportunity to enter a selling trade, potentially down to the $173 level.
Using this breakout strategy, traders can effectively capitalise on significant price movements. Setting appropriate stop-loss orders helps manage risk, ensuring that losses are limited if the breakout move reverses.
3. Responding to Economic News: Impact on Gold Trading
Keeping a close eye on economic updates allows traders to capitalise on market fluctuations. Positive economic reports can spur buying actions, while negative news may prompt selling.
Gold's Reaction to Employment Data
Following the release of a strong Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report, gold prices experienced a significant decline. As seen in the chart, a sharp bearish movement occurred, with gold dropping approximately 2.6% or nearly $60 per ounce, moving from around $2380 to $2320.
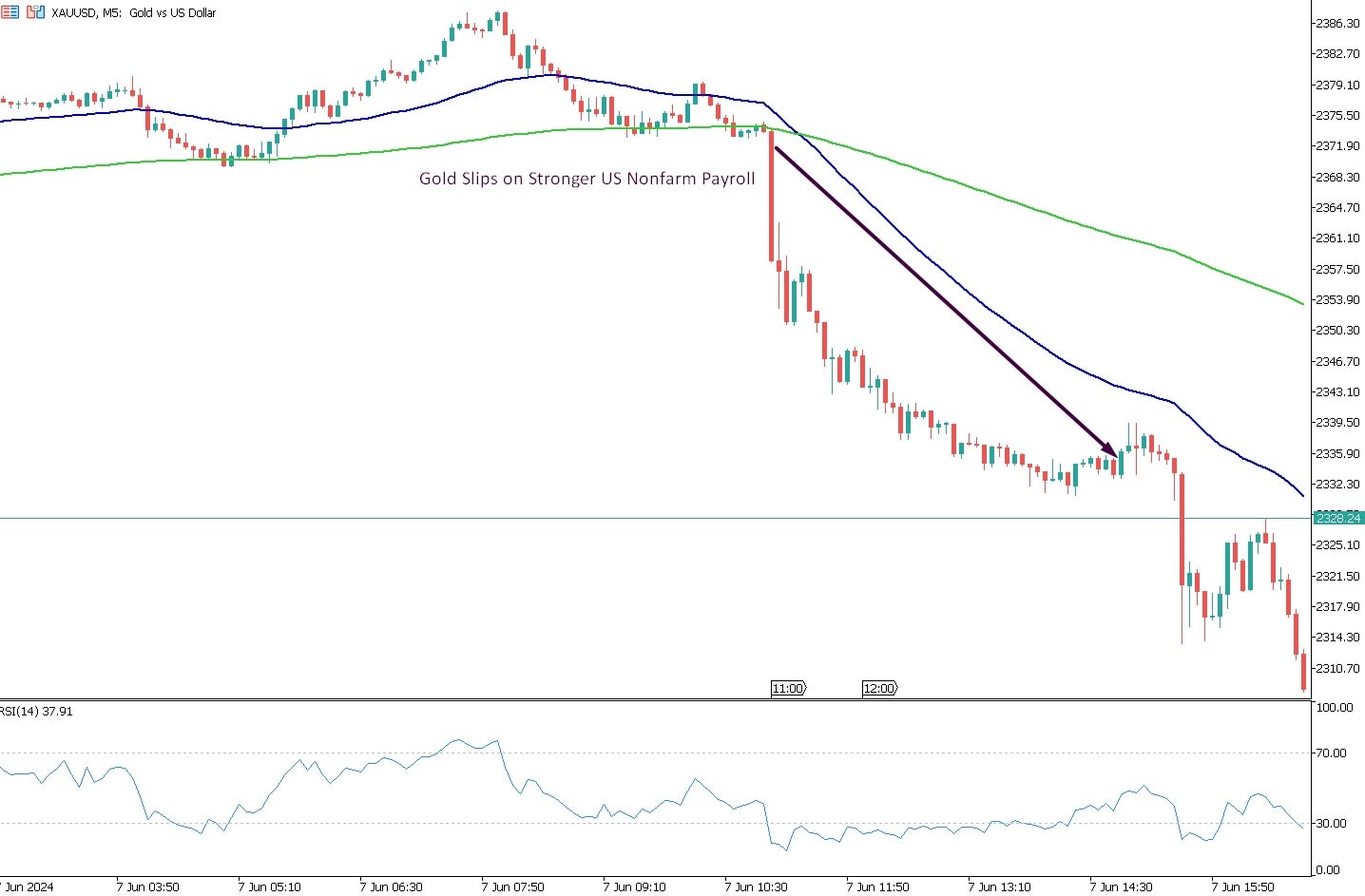
Explanation of Economic Figures and Market Reaction
The economic data released showed:
- Average Hourly Earnings increased by 0.4%, exceeding the forecast of 0.3%.
- Non-Farm Employment Change was 272K, significantly higher than the expected 182K.
- Unemployment Rate rose slightly to 4.0%, above the anticipated 3.9%.

This strong job market data suggests an improving economy, which often leads to expectations of higher interest rates. Higher interest rates strengthen the U.S. dollar, making gold less attractive to trade. Consequently, gold prices fell sharply as traders adjusted their positions in response to the positive employment figures.
4. Hedging Against CFD Trading Risks
When trading CFDs, hedging involves opening two opposing positions on the same asset to minimise overall risk. If the market moves against one position, the other can help offset some losses.
For example, a trader holding a long position in gold might open a short position to hedge against potential declines. However, it is crucial to conduct deep analysis and determine your exit strategy before initiating hedging positions.
5. Adjusting Position Sizes in Volatile Markets
In volatile markets, adjusting your position size can help manage risk more effectively. By reducing your position size, you can limit potential losses. Align your position size with your risk tolerance and the asset's volatility.
For instance, if you usually trade 100 shares of a stock, consider trading 50 shares during high market volatility to reduce exposure.
6. Scalping for Quick Gains in CFD Trading
Scalping is a strategy for traders who prefer quick trades. It involves making numerous trades for small price gains, aiming to capitalise on minor price movements. For example, a scalper might buy and sell a currency pair within minutes to take advantage of a slight price increase. This approach reduces exposure to large market swings by entering and exiting positions swiftly.
Using these strategies, traders can better navigate volatile markets, potentially increasing returns while reducing risks in CFD trading.
Managing Liquidity Risks in CFD Trading
In this section, we’ll explore the concept of liquidity risk in CFD trading and its impact on your trading experience. Understanding liquidity risk is crucial for developing effective trading strategies and managing risks.
Understanding Liquidity in CFD Trading
Liquidity in CFD trading refers to how quickly and easily you can open or close positions without causing significant price changes. High liquidity allows for smooth trade execution, while low liquidity can result in substantial price alterations.
Here’s a concise breakdown:
- Liquidity: The ability to trade CFDs promptly at stable prices.
- High Liquidity: Facilitates smoother trading and better price stability.
- Variation: Liquidity levels vary across different CFD providers and market situations.
- Importance: A deep understanding of liquidity is vital for effective trading strategies and risk management.
To mitigate risks, always assess the liquidity of your chosen CFDs before trading.
Liquidity Impact on Trade Execution
For beginners in forex and CFD trading, liquidity affects how easily you can buy or sell an asset without significantly impacting its price. Here's why it's important:
Slippage: This occurs when a trade is executed at a different price than expected due to a lack of immediate buyers or sellers. Slippage can reduce gains or increase losses. For example, if you plan to buy a CFD at $100 but it executes at $102 due to low liquidity, that $2 difference can impact your overall returns.
Wider Spreads: In less liquid markets, the spread—the difference between the buying and selling price—widens. For instance, a spread might increase from 1 pip to 5 pips, making it more expensive to enter or exit trades, thus reducing potential returns.
Increased Volatility: Low liquidity can lead to larger price swings, making the market more unpredictable and challenging to manage. For example, in a less liquid market, a sudden news event might cause a 10% price jump, compared to a 2% jump in a highly liquid market.
Exiting Challenges: In low liquidity conditions, selling your position quickly or at your desired price can be difficult. During significant news events, liquidity can dry up, leaving you stuck in a position. For example, if a market opens with a gap due to overnight news, you might find it hard to sell your position at the expected price, leading to potential losses.
Example: The Importance of Liquidity
Imagine you're trading CFDs on a lesser-known stock with low liquidity. You buy 100 shares at $50 each, expecting to sell them at $55. However, due to low liquidity, when you decide to sell, the best available price is $48. This results in a $200 loss instead of the anticipated $500 gains.
Managing Counterparty Risk in CFD Trading: The Broker Factor
In CFD trading, the reliability of your broker is a critical factor. Brokers serve as intermediaries, so their financial stability and order execution capabilities are crucial for traders. Here's an overview of the role brokers play and how they can impact your trading experience.
The Importance of Broker Reliability
Execution Dependence
Traders rely on brokers for accurate and timely order execution. Technical glitches or slow order processing by the broker can result in missed trades or losses. For instance, if you place a buy order for a CFD at $100, but due to a technical issue, the order executes at $105, you’ve already incurred a loss.
Order Routing Practices
Some brokers may prioritise their interests over clients', affecting potential gains. It's essential to choose a transparent and fair broker to ensure just treatment. For example, a broker that routes orders in a way that benefits them over the trader can lead to less favourable trade prices for you.
Broker Solvency
A broker's financial health is vital. If a broker becomes insolvent, traders risk losing their deposits and any open positions. For instance, if you have $10,000 deposited with a broker and they go bankrupt, you might lose your entire deposit.
Minimising Broker Solvency Risk
- Research Thoroughly: Conduct extensive research before selecting a broker.
- Regulated Brokers: Opt for brokers regulated by reputable authorities, ensuring they follow strict financial standards and keep client funds in segregated accounts.
- Diversification: Use multiple regulated brokers and regularly review their financial health and regulatory standing.
Example: Choosing a Reliable Broker
Imagine you're trading CFDs on the forex market. You select a broker regulated by a top-tier authority, such as the FCA or ASIC, which ensures your funds are held in segregated accounts and the broker adheres to strict financial standards. This reduces the risk of losing your capital due to broker insolvency and provides peace of mind regarding fair order execution.
Essential Risk Management Strategies in CFD Trading
Risk management is the foundation of effective CFD trading within the financial market. Here’s a concise guide to help traders protect their capital and maximise long-term gains.
Utilise Stop-Loss Orders
Setting stop-loss orders is a fundamental risk management tool in CFD trading. A stop-loss is a predetermined price point that triggers an automatic sell-off to prevent steep losses. For instance, if you buy a CFD at $100 and set a stop-loss at $95, the position will automatically close if the price drops to $95, helping you stick to your risk thresholds and avoid emotional decision-making.
Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification is a smart strategy in CFD trading. Instead of putting all your capital into a single asset, spread it across various assets or markets. For example, you might trade in CFDs on forex, commodities, and stocks. This way, potential losses in one area may be offset by gains in another, balancing the overall risk.
Stay Informed
Being well-informed is crucial for effective risk management. Understanding market dynamics, economic indicators, and global events allows traders to anticipate market shifts and adapt strategies promptly. For instance, staying updated on non-farm payroll reports or geopolitical events can help you make informed decisions and adjust your trading positions accordingly.
Example: Risk Management in Practice
Imagine you are trading CFDs on the forex market. You diversify your portfolio by trading in different currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and AUD/USD. You set stop-loss orders for each position to limit potential losses. Additionally, you stay updated on economic news and global events that might affect currency prices. By implementing these strategies, you can navigate the market's volatility and protect your trades.
Managing Psychological Risks in CFD Trading: Emotional Trading and Overtrading
Managing psychological risks is crucial for effectiveness in CFD trading. Recognising and analysing emotional biases, employing self-control techniques, and maintaining disciplined risk management can help traders overcome challenges and enhance their results.
Recognising Emotional Biases in CFD Trading
Effective trading is not only about strategies but also about managing your psychology. Recognising and overcoming emotional biases is key to disciplined trading and long-term growth.
- Acknowledge Emotional Biases: Emotions like fear and greed can cloud judgment. Recognising these feelings helps prevent rash decisions not based on market realities.
- Avoid FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): FOMO can lead to impulsive trades. It’s crucial to enter trades based on analysis, not fear of missing out on gains.
- Curb Greed: Greed can tempt traders to ignore risk management and aim for unrealistic returns, increasing the likelihood of significant losses.
- Check Overconfidence: Overconfidence may lead to underestimating risks and overvaluing one's abilities, resulting in poor decision-making.
Strategies to Maintain Trading Discipline
Maintaining discipline is essential for managing psychological risks in trading. Here are some strategies:
Create a Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan acts as your blueprint for trading. It should detail when to enter or exit trades, risk limits, and trading goals. By adhering to your plan, you can navigate market ups and downs without falling prey to emotions.
Example Trading Plan Criteria:
- Entry Criteria: Define conditions to enter a trade. Example: Buying a stock when its 50-day moving average crosses above its 200-day moving average.
- Exit Criteria for Gains Determine when to exit a trade. Example: Selling a stock when it reaches a 20% gain from your entry point.
- Exit Criteria for Losses (Stop-Loss Orders): Decide in advance how much you are willing to lose and set a stop-loss order. Example: Setting a stop-loss order at 10% below your purchase price.
- Risk Management Rules: Specify how much of your total capital you are willing to risk on a single trade. Example: Risking no more than 2% of your total trading capital on any single trade.
- Exit Targets: Set clear targets for exiting trades. Example: Aiming for a target of 15% above your entry price.
- Market Analysis Method: Outline which analysis methods you will use. Example: Using technical analysis to identify trending stocks and fundamental analysis for long-term trades.
- Trading Time Frame: Specify whether you'll be day trading, swing trading, or position trading. Example: Swing trading with trades lasting from a few days to several weeks.
- Asset Classes and Instruments: Define which markets or securities you'll trade. Example: Focusing exclusively on forex pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD.
- Review Schedule: Plan regular reviews of your trading plan. Example: Conducting a weekly review of your trading activities and plan effectiveness.
Exercise Patience
Patience is crucial in trading. Resist the urge to trade on a whim; wait for opportunities that align with your strategy. Trading out of fear or excitement often leads to poor outcomes.
Apply Risk Management
Implement strict risk management to curb emotional trading. Set trade sizes that fit your risk tolerance, use stop-loss orders to cap potential losses, and ensure potential rewards justify the risks taken.
Manage Emotions
Emotional control sets effective traders apart. Use techniques like meditation, journaling, or seeking mentorship to understand and regulate your emotions, particularly during volatile market times.
Learn from Experience
Every trade, win or lose, offers a chance to grow. Regularly review your trades to identify what worked and what didn’t. This self-reflection will sharpen your decision-making and reinforce discipline in your trading approach.
Conclusion
Traders venturing into CFD trading should approach it with an informed and open-minded perspective. Effective risk management is essential—setting stop-loss orders, diversifying positions, and staying updated on market developments are key strategies to minimise losses and maintain long-term viability. Traders with strong discipline and the ability to overcome psychological biases are more likely to sustain effective trading practices. Employing a balanced strategy can help traders navigate challenges and achieve their financial goals.
At ACY Securities, we empower traders by providing:
- Education Tailored to You: Catering to traders of all levels, we offer a diverse range of educational resources.
- Informed Trading: We ensure you're not trading in the dark. Our expert insights and analysis support your trading decisions, helping you navigate the markets more confidently.
- Ready to Dive In? Open your account with us today and begin a journey of growth and learning. Embrace the opportunity to grow, learn, and excel in the dynamic trading landscape with ACY Securities.
Explore ACY Securities' expert-led webinars to help traders navigate the world of the forex market. Learn more about Shares, ETFs, Indices, Gold, Oil and other tradable instruments we have on offer at ACY Securities.
You can also explore our MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 trading platforms including access to our free MetaTrader scripts. Then try out your own trading strategies on your own free demo trading account.
FAQs
- What are the key risks associated with CFD trading? The key risks include market volatility, leverage, liquidity challenges, and counterparty risk, all of which can significantly impact your trading outcomes.
- How does leverage affect CFD trading? Leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses by allowing you to control larger positions with a smaller initial trade. For example, a 1:10 leverage means you only need 10% of the position’s value as margin.
- Why is understanding market volatility important in CFD trading? Market volatility indicates how much asset prices fluctuate. High volatility offers opportunities for quick gains but also increases the risk of significant losses.
- What is liquidity in CFD trading and why is it important? Liquidity refers to how quickly and easily you can trade an asset without significantly affecting its price. High liquidity allows for smoother trade execution and better price stability.
- How can traders manage psychological risks in CFD trading? Traders can manage psychological risks by recognising emotional biases, sticking to a disciplined trading plan, using stop-loss orders, and staying informed about market developments.
Try These Next











