How Interest Rates, Inflation, and Bonds Drive Forex Markets
2024-10-15 14:57:45
The relationship between interest rates, inflation, and bonds is pivotal in shaping the dynamics of the forex markets. When inflation rises, central banks like the Federal Reserve or the Bank of England may increase interest rates to control price growth. Conversely, lower inflation often leads to reduced interest rates, encouraging borrowing and economic activity.
Bonds also play a significant role in reflecting a country’s economic health. Typically, when interest rates rise, bond yields increase, indicating economic strength.
On the other hand, falling interest rates usually cause bond prices to rise, making bonds a more attractive option. These movements can influence the flow of foreign capital, affecting currency value in the forex markets.
Key points to consider include:
- Interest Rates: Central banks use interest rates to control inflation and stabilise the economy, directly impacting currency value.
- Inflation: High inflation may lead to increased interest rates, strengthening the currency, while low inflation can result in rate cuts and a weaker currency.
- Bonds: Changes in bond yields and prices reflect trader confidence in a country’s economic stability, influencing Forex traders’ decisions.
This article delves into the relationship between these elements, offering strategies to help traders effectively navigate these complexities.
Interest Rates: The Core Driver of Forex Movements
Interest rates are a key driver of Forex market movements, as they directly influence the value of currencies. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Bank (ECB), control interest rates through various monetary policies, such as open market operations. These actions impact short-term interest rates, influencing longer-term rates and economic activity.
When central banks cut interest rates, they loosen monetary policy, stimulating borrowing and spending. Conversely, when rates are raised, they tighten monetary policy to curb inflation and slow economic growth. This is why interest rates matter significantly in the forex market, as they can lead to substantial currency fluctuations.
Example for Better Understanding:
Let us consider a real-world example to illustrate how interest rates set by major central banks affect currency values. In March 2022, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 0.25% in response to escalating inflation in the United States.
This rate hike made the USD more attractive to traders as higher interest rates often lead to higher returns denominated in that currency.
As a result, the US dollar strengthened against other currencies, such as the Euro and the British Pound, impacting Forex traders and global financial markets.
For a deeper dive into practical strategies on interest rates, inflation, and bonds in the forex market, watch the video below:
Impact of Interest Rates on Forex Trading
- Central Bank Influence
Forex traders closely monitor central bank meetings and policy updates from institutions like the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank. Interest rate changes can trigger immediate and significant currency fluctuations. - Economic Indicators
A country’s interest rate decisions reflect its economic outlook. Rate hikes usually indicate economic strength, while cuts can signal economic concerns or the need to stimulate growth. - Interest Rate Differential (IRD)
- The IRD represents the difference between the interest rates of two currencies in a pair.
- Traders use IRD to gauge potential gain opportunities through carry trades—borrowing in a low-yield currency (e.g., JPY) and trading in a high-yield currency (e.g., AUD).
- Changes in IRD can make a currency attractive, influencing trading decisions and demand.
Inflation: The Silent Currency Mover
What is Inflation?
- Inflation is the gradual loss of purchasing power, reflected in rising prices of goods and services over time. It is measured by tracking the annual percentage change in a basket of essential items like food, housing, and healthcare.
- Higher inflation reduces a currency’s value, making it less attractive in the Forex market.
Healthy Inflation Rates:
- A modest, low single-digit inflation rate (around 2%) is considered healthy for the economy. It encourages spending, which supports economic growth.
- Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, aim to keep inflation controlled to maintain long-term economic stability.
Key Inflation Indicators:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): This index measures price changes from the consumer's perspective, showing how much consumers are paying for the same basket of goods and services.
- Producer Price Index (PPI): This index reflects price changes from the seller’s perspective, indicating changes in production costs that could influence future CPI.
Impact on Monetary Policy:
- Central banks use CPI and PPI data to guide their monetary policies. Rising inflation often leads to interest rate hikes to curb spending, while falling inflation may trigger rate cuts to stimulate the economy.
Impact of Inflation on Central Bank Policies
Central banks, such as the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) in the United States, use interest rate adjustments to manage inflation. During the global financial crisis of 2008, central banks around the world adjusted their interest rates to manage economic downturns and inflation.
When inflation rises above the target rate, central banks raise interest rates to cool down the economy and curb excessive spending.
This strategy helps maintain price stability and strengthens the national currency, as higher interest rates attract foreign interests.
For example:
- In 2022, U.S. inflation hit 9.1%—a 40-year high.
- To tackle this, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates multiple times, starting with a 0.25% hike in March, followed by several 0.75% increases.
- These rate hikes were intended to bring inflation down and stabilise the value of the U.S. dollar.
How Inflation Influences Forex Trading
Inflation plays a crucial role in Forex trading by impacting currency value and shaping trader behaviour. Here is how it works:
Currency Depreciation:
- High inflation decreases purchasing power, weakening a currency.
- Example: In 2022, Turkey's annual inflation surged to 80%, causing the Turkish Lira (TRY) to plummet by over 40% against the USD. As a result, the TRY lost significant value in the Forex market.
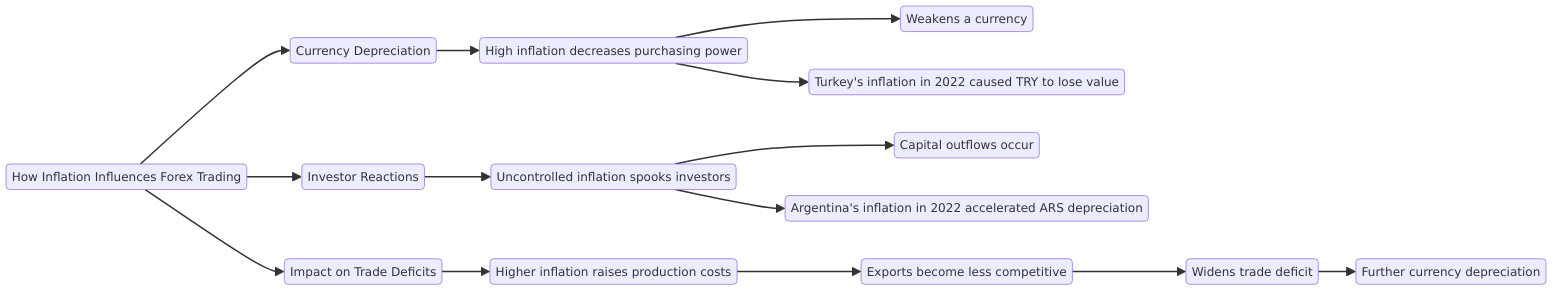
Trader Reactions:
- Uncontrolled inflation can spook traders, leading to capital outflows.
- Example: When Argentina's inflation hit 94.8% in 2022, foreign traders quickly pulled out, accelerating the Argentine Peso's depreciation.
Impact on Trade Deficits:
- Higher inflation raises production costs, making exports less competitive.
- This often widens a country’s trade deficit, causing further currency depreciation.
Forex Trading Tip: Traders watch inflation reports like the CPI and PPI closely. If U.S. inflation spikes, for example, traders may buy USD and sell currencies like the Euro (EUR) or Japanese Yen (JPY), expecting the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates, thereby strengthening the USD.
Learn more about trading strategies in our Education blog. Explore the core economic forces that move the forex market—interest rates, inflation, and bond yields—and learn how shifts in these areas impact currency strength and trading opportunities. Watch the video below:
Bonds and Their Role in the Forex Market
Government bonds are debt securities issued to fund a nation’s spending. When a trader buys a bond, they lend money to the government in exchange for periodic interest payments, known as coupons. This steady income makes bonds attractive, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
The Federal Reserve, for example, uses government bond yields to control the money supply. When the Fed buys U.S. government bonds, it injects liquidity into the economy, giving banks more capital to lend. This can stimulate spending. Conversely, when the Fed sells bonds, it absorbs excess cash, reducing economic activity.
Example: In June 2024, U.S. 10-year Treasury yields dropped to 4.2% after the Fed indicated a possible rate cut. This decline showed that traders were expecting slower economic growth or lower future returns.
Bond Yields and Interest Rates: How They Interact
Higher Interest Rates = Higher Bond Yields
- When central banks raise interest rates, newly issued bonds must offer higher yields to attract buyers.
- Example: If the Federal Reserve increases rates from 4% to 5%, a $10,000 bond would need to provide a 5% yield, or $500 annually, to remain competitive.
- Higher yields make bonds more attractive, leading to increased demand and a stronger currency.
Lower Interest Rates = Lower Bond Yields
- When rates are cut, bond yields decline, making bonds less lucrative.
- This may cause traders to seek better returns in other markets or currencies.
- Example: If U.S. bond yields drop to 3% while UK yields stay at 4%, traders might sell USD to buy GBP, resulting in a weaker dollar.
Impact on Forex Market
- Changes in bond yields influence currency values as traders shift capital based on expected returns.
- Rising bond yields often lead to a stronger currency, while falling yields can weaken it, affecting exchange rates globally.
Impact of Bond Yields on Forex Trading
When bond yields rise, they can strengthen a currency as they attract foreign traders who must buy the local currency to trader in those bonds. For example, if U.S. Treasury yields rise to 5%, traders might buy more USD, pushing the dollar’s value higher.
Conversely, falling bond yields can weaken a currency. When yields decrease, the currency becomes less attractive, leading traders to seek alternatives. If the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield falls to 2%, while German Bunds offer 3%, traders might sell USD to buy Euros, expecting the EUR to strengthen.
Key Takeaways for Forex Traders
- Higher Bond Yields = Stronger Currency
Rising yields signal potential interest rate hikes and economic growth, making the currency more appealing. - Lower Bond Yields = Weaker Currency
Declining yields may indicate rate cuts or economic slowdown, leading to a weaker currency.
How Interest Rates, Inflation, and Bonds Interact to Influence Forex
Interest rates, inflation, and bond yields are interconnected and have a direct impact on currency movements in the Forex market. When central banks adjust interest rates, bond yields often move in the same direction, affecting trader demand for that country’s currency.
Inflation, in turn, plays a role in these adjustments, as central banks use interest rate changes to keep inflation in check, influencing bond yields and currency strength.
Case Study: The U.S. Bond Market’s Effect on USD in 2024
The U.S. bond market is a key player in determining the value of the U.S. Dollar (USD). In 2024, the Federal Reserve surprised markets by cutting interest rates by 50 basis points—an effort to counter declining inflation and economic slowdown.
Contrary to expectations, the 10-year Treasury yield increased by 17 basis points after the Fed’s decision. This spike occurred because traders anticipated that inflation could rebound, making long-term bonds less attractive.
As a result, demand for the USD increased as traders sought to benefit from potential future rate hikes, strengthening the currency.
Example: The 2013 “Taper Tantrum”
In 2013, the Federal Reserve hinted at reducing its bond-buying program. This announcement caused U.S. bond yields to rise sharply, as markets expected tighter monetary policy. As yields climbed, foreign traders began buying more USD to trade in U.S. bonds, pushing up the dollar’s value.
This event, known as the “Taper Tantrum,” illustrates how changes in bond yields, driven by central bank actions, can lead to significant shifts in currency values.
These examples show how bond yields, interest rates, and inflation data influence Forex trading decisions and currency trends. Traders who monitor these metrics closely can better understand the factors driving currency movements and position themselves accordingly.
Forex Trading Strategies Based on Interest Rates, Inflation & Bonds
Interest rates, inflation, and bond yields influence Forex trading strategies. By understanding how these elements interact, traders can create targeted strategies to capitalise on market shifts. Below are some common strategies used by Forex traders:
Carry Trade Strategy: Leveraging Interest Rate Differentials
The carry trade strategy involves borrowing in a currency with a low interest rate and trading in one with a higher yield. This allows traders to earn the difference in interest rates.
- Example: If Japan's interest rates are near zero while Australia's rates are around 3%, a trader might borrow Japanese yen (JPY) and convert it to Australian dollars (AUD) to trade in Australian bonds or assets. The trader then benefits from the higher yield in AUD compared to the borrowing cost in JPY.
Inflation Hedge Strategy: Trading in Inflationary Environments
Inflation can significantly impact currency values. Traders use the inflation hedge strategy to trade currencies of countries with low, stable inflation or those actively combating high inflation.
- Example: In 2021, Turkey experienced severe inflation, causing the Turkish Lira (TRY) to depreciate rapidly. To hedge against this risk, traders shifted their interests to currencies like the U.S. Dollar (USD) or Swiss Franc (CHF), which were more stable and protected against inflationary pressures.
Bond-Yield Differential Strategy: Using Bond Yields to Predict Forex Moves
Bond yields are closely tied to interest rate expectations and can indicate future currency strength. Traders track the bond yields of different countries and compare them to identify opportunities.
- Example: If U.S. Treasury yields rise above German Bund yields, it may signal that the Federal Reserve is likely to raise interest rates, potentially strengthening the USD against the Euro (EUR). Forex traders might then take a long position on the USD/EUR pair, anticipating a stronger dollar.
Key Economic Indicators to Watch for Forex Traders
Effective Forex trading involves keeping a close eye on economic indicators that can drive market movements. Some of the key indicators include:
- Interest Rate Decisions: Central banks regularly announce changes in interest rates. An interest rate hike often strengthens a currency by attracting foreign capital, while a rate cut can weaken it. Traders should analyse central bank statements and economic conditions to anticipate these moves.
- Inflation Metrics (CPI and PPI): The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) are essential for assessing price changes. Rising CPI can indicate higher inflation, potentially leading to interest rate hikes, while declining PPI might suggest lower production costs and easing inflation.
- Bond Auctions and Yields: Bond auctions reveal trader confidence and impact bond yields. Strong demand for a country’s bonds results in lower yields, supporting the currency. Conversely, weak demand can drive yields up and weaken the currency.
Conclusion
The interplay between interest rates, inflation, and bond yields is fundamental to understanding currency movements in the Forex market. As central banks adjust interest rates to control inflation, the value of currencies fluctuates based on trader expectations and capital flows.
Traders can leverage strategies like carry trades, inflation hedges, and bond-yield analysis to capitalise on these shifts.
By staying informed and tracking key economic indicators, traders can make more accurate decisions and effectively manage risk in a dynamic market environment.
With ACY Securities, you receive more than just a platform for trading; you gain access to a comprehensive suite of educational resources and expert-led webinars to sharpen your trading skills and confidently manoeuvre through the complex financial landscape. Deepen your forex understanding and improve your trading with ACY Securities. Trade in a liquid market today.
At ACY Securities, we empower traders by providing:
- Education Tailored to You: Catering to traders of all levels, we offer a diverse range of educational resources.
- Informed Trading: We ensure you are not trading in the dark. Our expert insights and analysis support your trading decisions, helping you navigate the markets more confidently.
- Ready to Dive In? Open your account with us today and begin a journey of growth and learning. Embrace the opportunity to grow, learn, and excel in the dynamic trading landscape with ACY Securities.
Explore ACY Securities expert-led webinars to help traders navigate the world of the forex market. Learn more about Shares, ETFs, Indices, Gold, Oil, Forex, Futures, and other tradable instruments we have on offer at ACY Securities.
You can also explore our LogixTrader, MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 trading platforms including access to our free MetaTrader scripts. Then try out your own trading strategies on your own free demo trading account.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do interest rates affect Forex trading?
- Higher Interest Rates = Stronger Currency:
When central banks raise interest rates, foreign traders are drawn to the higher returns, increasing demand for the currency. - Example: In 2023, a 0.5% rate hike by the Federal Reserve led to a 2% increase in the value of the USD against the EUR.
2. What is a carry trade strategy in Forex trading?
- A carry trade involves borrowing in a low-interest currency and trading in one with a higher yield.
- Example: Bqorrowing Japanese yen (JPY) at 0.1% and buying Australian dollars (AUD) at 3% yield can yield gains from the 2.9% interest rate difference.
3. How do inflation rates influence currency values?
- High inflation erodes purchasing power and weakens the currency.
- Example: In 2022, Turkey’s 80% inflation rate caused the Turkish Lira (TRY) to lose over 40% of its value against the USD.
4. Why are bond yields important in Forex trading?
- Rising bond yields often signal potential interest rate hikes, making the currency more attractive.
- Example: When U.S. 10-year Treasury yields rose from 1.5% to 2%, the USD gained 1.7% against the EUR.
5. How do central bank decisions impact Forex trading?
- Rate hikes typically strengthen a currency, while rate cuts can weaken it.
- Example: A surprise 0.75% rate cut by the Bank of England in 2021 caused the GBP to drop 3% against the USD.
6. What economic indicators should Forex traders monitor?
- Key indicators include CPI, PPI, GDP, and unemployment rates.
- Example: A 5% increase in U.S. GDP growth led to a 2% appreciation of the USD as traders expected rate hikes.
7. How does the bond-yield differential strategy work in Forex trading?
- Traders compare bond yields between countries to predict currency moves.
- Example: In 2023, a 0.5% increase in U.S. yields over German Bunds led to a 2% rise in USD/EUR as traders shifted to the higher-yielding USD.
Try These Next











