Navigating Forex Markets using Dow Theory: An In-depth Guide
2023-07-06 15:35:07
Even in our technologically advanced age, some traders continue to rely on time-tested methods for technical analysis. Among these, the Dow Theory holds a prominent place as one of the earliest and most respected analytical models. The foundation of this theory dates back over a century, tracing its origins to the work of Charles Dow, who shared his perspectives in the Wall Street Journal in the early 1900s.
While Charles Dow himself did not formally present his insights as a theory, his successors, most notably William Hamilton, further developed and refined Dow's ideas posthumously, resulting in the Dow Theory we know today. Today, the Dow Theory remains an integral part of technical analysis, applicable in diverse financial markets, including Forex trading.
Though the Dow Theory we use today has evolved over its century-long history, its essence remains significant in the present-day Forex market dynamics.
At ACY Securities, we recognise the enduring relevance of these traditional techniques in trading. In this guide, we will unpack the Dow Theory and illustrate its various market phases. We will also introduce some effective Dow Theory-based chart reading strategies that Forex traders can utilise to optimise their trading strategies.
Understanding the Dow Theory: What Does It Mean?
Dow theorised that the stock market as a collective entity serves as a precise barometer of the trajectory of the economy's business health. By scrutinising the broad market, one can effectively gauge such scenarios, ascertain notable market trends, and forecast the anticipated motion of specific equities.
According to Dow, a market is in an ascending trend if one of its averages rises above a prior notable high and then experiences a parallel increase in another average. For instance, if the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) soars to an exceptionally high level, the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) will emulate this surge within a brief period.
As per Dow Theory, the combined movement of the DJIA and DJTA indices presages the direction of the trend. A bullish trend is assumed when the two indices move synchronously, leading to escalating lows followed by consecutively ascending highs.
How Does the Dow Theory Work?
Dow Theory is a collection of guiding principles that aid investors in understanding market trends. These six fundamental tenets of the Dow Jones can enable investors to make more informed decisions in both bullish and bearish market conditions.
Swift Response of Asset Prices to News
This theory aligns with the efficient market hypothesis, suggesting that the current price of an asset encapsulates all publicly available information. Even if an individual does not delve into related market data, the currency will respond to the latest news sentiment.
Investors need to predict future outcomes using both reactive and anticipatory information. However, there is no guarantee that the market will reflect the emotions of recent news events.
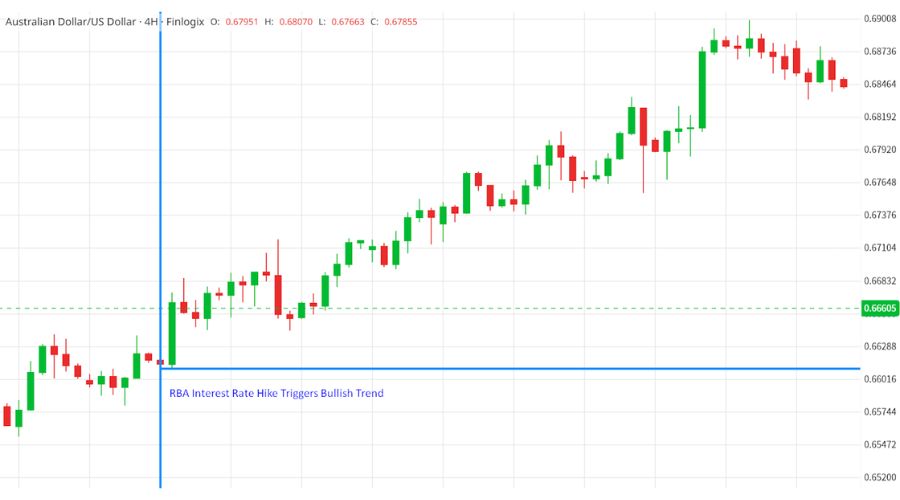
For instance, during a meeting on June 6th, the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) raised the Cash Rate from 3.85% to 4.10%. This news led to a significant surge in the AUD/USD exchange rate that day. Such monetary policy decisions can have a direct impact on the value of a currency, as seen in this scenario.
Dive deeper into understanding the Dow Theory here:
The Three Primary Types of Forex Market Trends
Dow divided trends into three types based on their duration:
1. Primary Trends
The major trend is the market's primary trend, indicative of the market's long-term direction and can continue for several years.
2. Intermediate Trends
Intermediate trends are counter-movements to a major trend. They act as a reversal of the prevailing trend. For instance, if the major trend is upward (bullish), the intermediate trend would be downward (bearish). These patterns may persist anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
3. Minor Trends
Minor trends are daily fluctuations in the market's movement. These trends are short-lived (typically less than three weeks) and move against the intermediate trend's direction. Some analysts suggest that minor trends reflect market speculation.
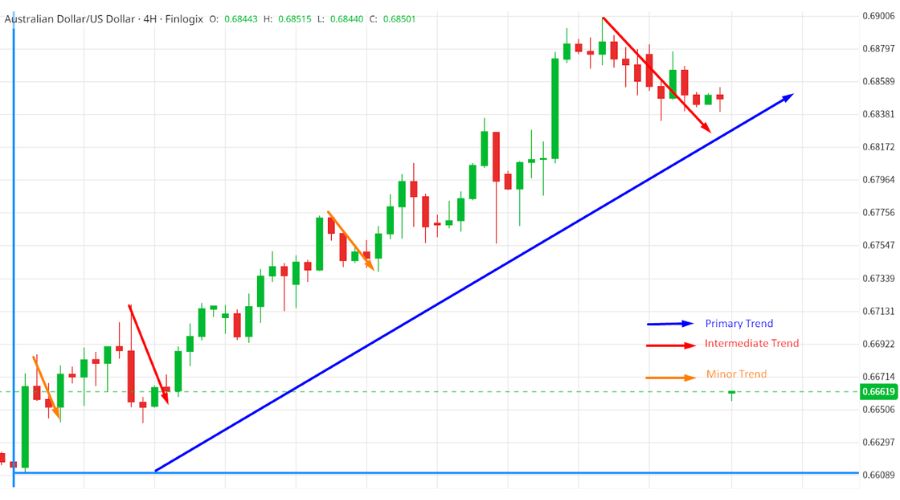
The chart above shows a weekly AUD/USD chart with an upward major trend. Some downward corrections, which are recognised as intermediate trends, are shown within this upward trend.
Three Stages of Primary Trends
The Dow Theory proposes that a major trend will progress through three stages.
1. The Accumulation Stage
The accumulation stage signifies the onset of a rising or falling trend in a bull or bear market. At this point, traders begin to enter the market to purchase or sell assets contrary to the general market sentiment.
2. The Public Participation
As market conditions improve and positive sentiment becomes more prevalent, more investors start participating in the market during the public involvement stage. This leads to a rise or fall in market prices.
3. The Panic Stage
The panic stage is characterised by heightened buying activity among investors. Numerous traders attempt to augment their gains through speculation, but early entrants recognize the diminishing trend and decide to exit their positions.
Trends Persist Until a Significant Reversal Happens
It can be challenging to differentiate between reversals in primary and secondary trends. The Dow Theory promotes patience, advocating for clear evidence of a potential reversal before acting. It is not always easy to ascertain if a surge in a bear market represents a reversal or merely a brief rally preceding even deeper lows.
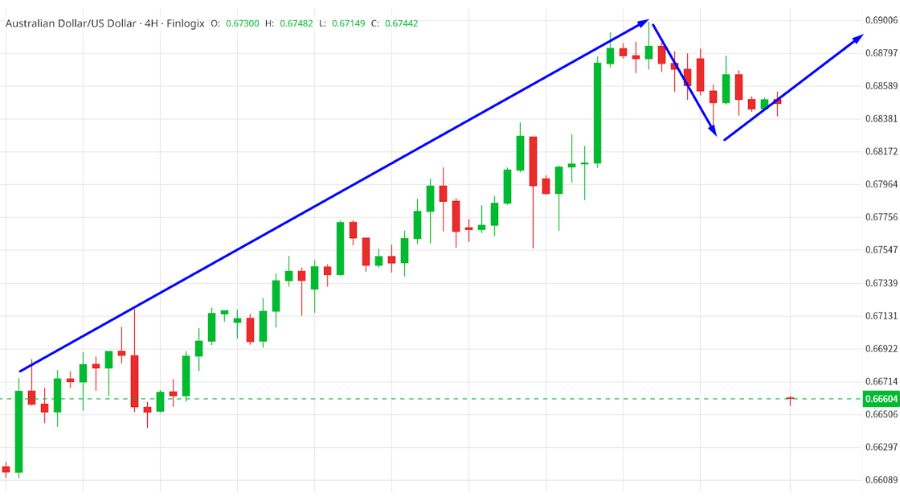
According to the Dow Theory, primary trends will consistently display short-term noise moving in the opposite direction. Trends will persist as long as there are no conspicuous reversal indications.
For instance, the AUD/USD 4-hour chart above illustrates how the price continues to ascend despite a 30% sell-off, thanks to a powerful uptrend.
This reinforces the idea of initiating trading positions aligned with the direction of the primary trend and resisting any temptations to trade against it.
Indices Should Confirm Trends
Charles Dow proposed that a trend identified in one market's average must be confirmed by a trend in another market. If a trend emerges in one market index but is not mirrored in any other market average, it is just noise. The fundamental premise of this approach is that the indices stemming from good production and sales are interconnected.
For instance, moving physical goods from storage facilities involves transportation. Consequently, a drop in transportation stocks would result in a fall in industrial stock prices. Therefore, transport and industrial averages should ideally move in unison to represent consistent market sentiment. A divergence happens when one index ascends while the other descends. This could signify an impending change in the current market trend.
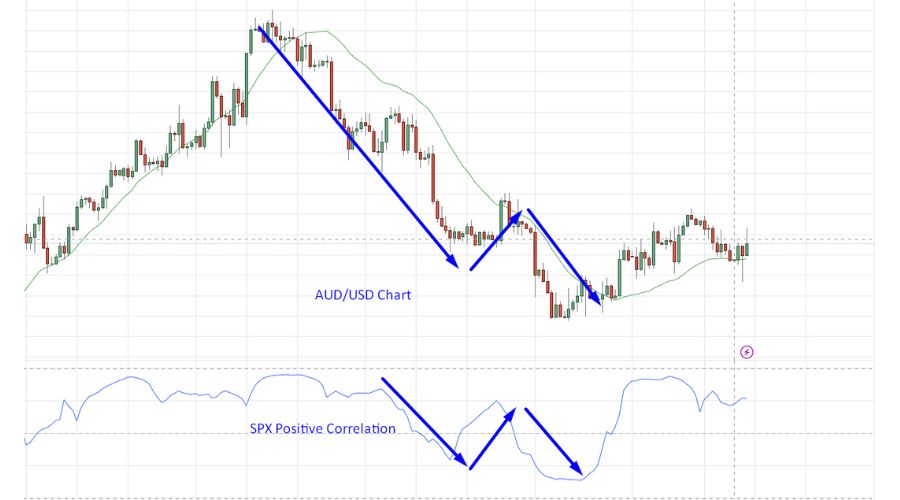
Investors can anticipate the direction of the Forex market by comparing it to other indices such as the S&P 500, FTSE, or NASDAQ. The daily AUD/USD chart above reveals the correlation between the DJI and the SPX. They show a positive correlation as they move coordinated.
Volume Must Support a Trend
According to Dow Theory, if the market moves in the direction of the primary trend, the volume should escalate; conversely, if the market moves against it, the volume should decline. A reduced volume suggests a deteriorating trend. In a bull market, the volume should amplify as prices ascend and diminish during subsequent retracements.
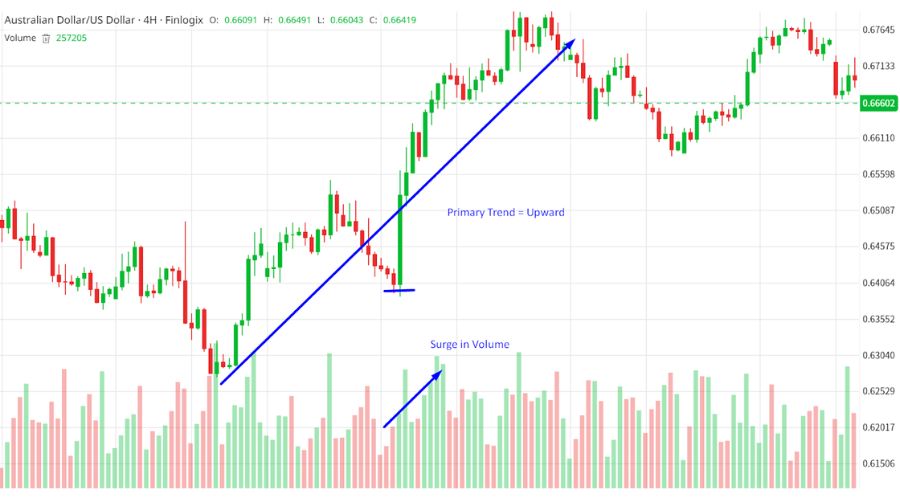
The chart illustrated above demonstrates that the volume increased due to the robust primary trend. This example signifies that the volume is mirroring the primary trend.
Implementing Dow Theory in Forex Markets
1. Primary and Secondary Trends
To exploit profitable price trends, let us incorporate Dow Theory into the Forex market, specifically focusing on the primary trend. Given the relatively nascent status of cryptocurrency markets compared to traditional Forex markets, the primary trend is easier to distinguish.
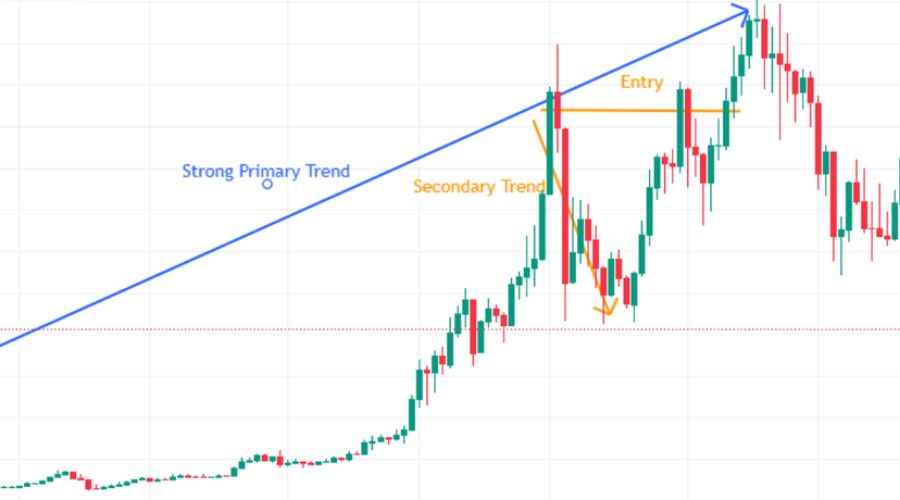
The above weekly AUD/USD chart illustrates a bullish primary price trend and a bearish secondary price trend. The chart demonstrates how the price dips during the second wave but swiftly rebounds once it surpasses the most recent upward swing. Consequently, there is an abrupt surge in price due to bullish pressure.
According to Dow Theory, traders should only initiate trades that align with the primary trend. In this instance, investors should be vigilant for the cessation of the secondary trend. The chart indicates that the bearish secondary trend will terminate when the price ascends above the most recent swing high.
2. Accumulation and Distribution
Investors must also make sure that volume indicators support the phases of accumulation and distribution for a more accurate trading entry. The following confirmations determine the buy entry in the above daily AUD/USD chart:
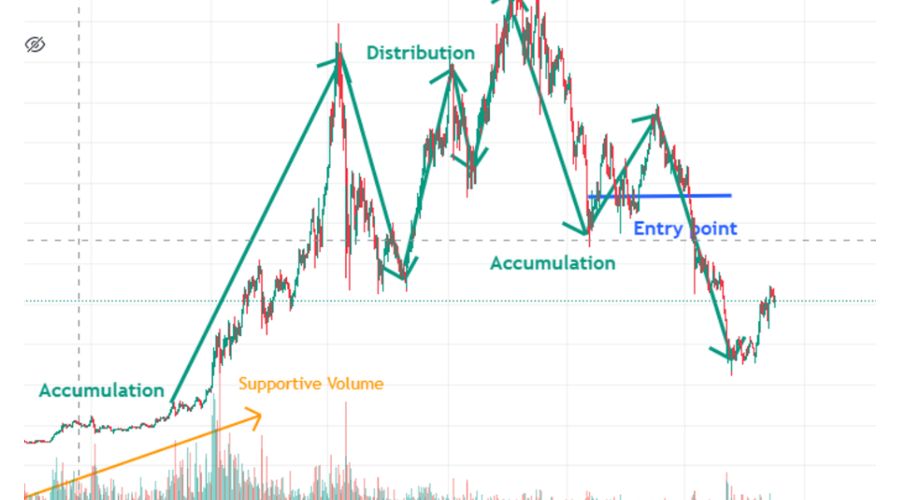
- The primary trend persists in its ascent.
- Volume predominantly favours the primary trend.
- The market has entered the accumulation stage following the completion of the distribution phase.
- A second swing high is overturning the secondary trend in this accumulation zone, which is bearish.
Drawbacks of Dow Theory
While the Dow Theory is the cornerstone of contemporary technical analysis, it possesses certain shortcomings.
- The criteria for detecting a shift in trend are excessively intricate.
- An overemphasis on minor price movements can occur when only closing prices are utilized.
- At least two years' worth of data is necessary for forecasting market trends based on supply and demand.
- This theory asserts that we cannot anticipate market trends in advance.
- It fails to provide an accurate portrayal of the magnitude of buyers and sellers.
- Dow Theory does not account for target levels.
- According to the Dow Theory, there is a delay between the actual inversion of a major trend and its acknowledgment.
- The theory does not recognize a turn until it has transpired and been validated.
Final Thoughts
Despite being more than a hundred years old, Dow Theory remains applicable in today's Forex trading landscape. Comprehending this theory can assist traders in identifying and seizing market trends, even though the complex nature of this concept can make the frequent correlations of multiple indices challenging.
Traders could, on the other hand, compare the price movements of closely related Forex pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, to decipher the market's overall sentiment. Even seasoned Forex traders need a well-crafted trading strategy, given the intrinsic volatility of the foreign exchange market. It is prudent for investors to remain cautious and utilise robust risk management techniques, even when investing their resources.
For those interested in deepening their understanding of Dow Theory and its application in Forex trading, ACY Securities offers comprehensive free educational resources and expert guidance to help give you an edge on your trading journey.
Try These Next











