Using Moving Averages for Trading: A Comprehensive Guide
2023-07-05 16:45:57
At ACY Securities, we understand the importance of technical trading indicators in the dynamic world of forex trading. Among these indicators, the moving average stands out as one of the most widely used and effective tools. As forex traders, it is crucial to analyse price trends and identify potential buying or selling opportunities accurately. This is where moving averages come into play. By calculating the average price of a currency pair over a specific time period, moving averages help smooth out short-term price fluctuations, providing traders with a clearer understanding of the overall trend.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different types of moving averages, explore their applications in forex trading, and offer valuable insights on how you can leverage them to enhance your trading strategy.
Let us embark on a journey to master the art of using moving averages in forex trading.
Purpose of Moving Averages in Forex Trading
Moving averages are used in trading for several reasons:
- Trend Identification: Moving averages are utilized to identify and validate the direction of a price trend. By calculating the average price over a specific time period, moving averages reveal whether the price is experiencing an upward trend, a downward trend, or trading in a range-bound fashion. Traders often use multiple moving averages with different periods to capture both short-term and long-term trends simultaneously.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Moving averages can act as support and resistance levels, indicating potential levels at which prices may find support or face resistance. When the price approaches a moving average from below, it may find support and experience a rebound or reversal. Conversely, if the price approaches a moving average from above, it may encounter resistance and potentially undergo a bearish reversal.
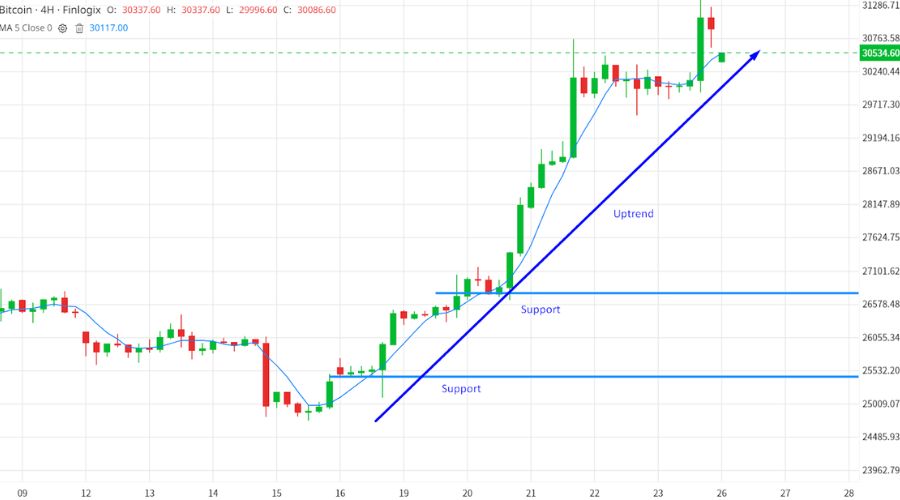
- Entry and Exit Points: Traders frequently use moving averages to identify optimal entry and exit points for their trades. A bullish signal is generated when a shorter-term moving average, such as the 50-day moving average, crosses above a longer-term moving average, like the 200-day moving average, indicating a potential buying opportunity.
Conversely, a bearish signal occurs when the shorter-term moving average crosses below the longer-term moving average, suggesting a potential selling opportunity.
- Price Smoothing: Moving averages help reduce price volatility by smoothing out short-term price swings, allowing traders to focus on the longer-term trend. This can provide a clearer view of the market's underlying trend while minimizing the impact of noise and false signals caused by temporary market fluctuations.
- Confirmation Tool: Moving averages are often used with other technical indicators or chart patterns as a confirmation tool for trading signals. By confirming signals from other indicators or patterns, moving averages can enhance the reliability of trade entries or exits.
By utilising moving averages in their analysis, traders can gain insights into trading opportunities, price patterns, and levels of support and resistance. Integrating these indicators into their decision-making process can improve their chances of success in the financial markets.
The Importance of Moving Averages in Technical Analysis
Moving averages hold significant importance in technical market analysis due to their ability to smooth price data, create trend lines, and provide a user-friendly tool for traders. They are highly compatible with price charts and other indicators, making them a valuable tool for analysing market trends.
The key reasons for the significance of moving averages in technical analysis are as follows:
- Predicting the availability of goods and commodities by using moving averages to anticipate minor trends or seasonality while maintaining steady demand.
- Distinguishing between random fluctuations in price movements.
- Identifying support and resistance levels by utilizing moving averages.
- Simultaneously plotting multiple moving average lines is simple and allows for easy interpretation.
- Consistency in forecasting through the use of moving averages.
By incorporating moving averages into their analyses, traders can spot trends, identify support and resistance levels, generate trading signals, and validate the accuracy of other indicators or patterns. This enables trading professionals to make informed decisions, optimize trade timing, and enhance overall trading success.
Types of Moving Averages
Moving averages may be divided into three categories:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
Each kind has unique properties and a calculating procedure that suits various trading styles and preferences. Let us examine each kind in more depth:
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The simplest form of moving average is the Simple Moving Average (SMA), also known as the Arithmetic Moving Average. The SMA calculates the average price of a forex pair over a specific time period by summing up the previous closing prices and dividing it by the number of data points or price periods. This provides the average price of the forex pair during that particular time frame.
The SMA is depicted in the graphic below and is created by calculating the average price of a financial market over a designated period of time.
Characteristics of SMA:
- Equal Weighting: Each data point within the calculation period is given equal weight in the SMA. It treats the earliest and most recent data values equally, resulting in a linear smoothing effect.
- Lagging Indicator: The SMA needs to catch up to current price fluctuations as it gives equal weight to all data points. It responds better to long-term patterns rather than short-term volatility.
- Smoothness: The SMA provides a smooth representation of price patterns by eliminating random noise and temporary price swings.
- Widely Used: The SMA is popular among traders due to its simplicity and readability. It is suitable for identifying trends, conducting support and resistance analysis, and generating trading signals.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
A more sophisticated type of moving average that provides greater emphasis on recent price data and is therefore more responsive to price changes is the Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The EMA calculates the average price by assigning a smoothing factor or weight to each data point, with higher priority given to the most current price data.
As shown in the image below, the EMA places more weight on recent prices and less weight on earlier values throughout the chosen time period.
Characteristics of EMA:
- Weighted Calculation: The EMA is designed to be highly responsive to new price swings as it assigns higher weight to recent data points. The smoothing factor, incorporated into the EMA calculation algorithm, determines the amount of weight assigned to each data point.
- Quick Response: Compared to the SMA, the EMA reacts more quickly to price changes. This makes it suitable for traders seeking shorter-term trends and faster alerts.
- Lag Reduction: By assigning more weight to recent prices, the EMA reduces the lag associated with the SMA. It is considered a more accurate indicator of the market's current state.
- Trend Identification: The EMA is particularly useful for identifying trends in their early stages or when the market experiences rapid price fluctuations.
Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
The Weighted Moving Average (WMA) differs from the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) by assigning varying weights to each data point during the calculation period. Unlike the equal or exponential weighting used in SMA and EMA, WMA utilizes a predetermined weight distribution.
As depicted in the image below, the WMA outperforms the SMA as a short-term indicator, providing a more responsive outcome better suited for intermediate or short-term trades.
Characteristics of WMA:
- Variable Weighting: WMA assigns different weights to the data points during the calculation period. The weight distribution can follow a linear, triangular, or other predetermined pattern.
- Adjustable Smoothing: Traders can adjust the smoothing effect of WMA to their preferences or market conditions.
- Sensitivity: The chosen weight distribution affects the sensitivity of WMA. Reactivity to price fluctuations may vary based on the weight distribution employed.
- Limited Usage: WMA is less commonly used compared to SMA or EMA. Traders who wish to emphasize specific periods or data points in the moving average calculation may opt for WMA.
Calculating Moving Averages: Understanding the Calculation Methods for Moving Averages
Regardless of the type of moving average used, the calculation process is relatively straightforward. The following is a general methodology for calculating moving averages:
- Determine the Period Length: Choose the desired period length for the moving average. This refers to the number of data points or periods the calculation includes. For example, a 10-day moving average considers the previous 10 data points or daily intervals.
- Collect the Price Data: Gather the price data for the selected forex pair within the chosen time frame. The closing price is the most commonly used price for calculations, although some traders may utilize alternative values such as high, low, or average prices.
- Sum the Data Points: Add up the selected price data points over the specified time period. For example, when calculating a 10-day moving average, add the most recent 10 closing prices.
- Divide by the Number of Periods: Divide the sum from Step 3 by the total number of periods (data points) considered. For a 10-day moving average, divide the total by 10.
- Repeat the Calculation: As new data becomes available, replace the oldest data point with the most recent one to update the moving average. Utilize the updated set of data to recalculate the moving average.
By following these steps, traders can calculate moving averages and use them as valuable tools for analysing price trends and making informed trading decisions.
Choosing the Appropriate Period Length for the Moving Average
Depending on the trading strategy, timeframe, and desired level of responsiveness, selecting the appropriate period length for a moving average is crucial.
Shorter period lengths, such as 10 or 20, offer greater sensitivity to recent market fluctuations but may also generate more false signals. On the other hand, longer period lengths, like 50 or 200, may lag price movements but provide a more reliable representation of long-term patterns.
Traders often experiment with different period lengths and adjust them based on the volatility of the forex pair, market conditions, and their individual trading style. Striking a balance between responsiveness and reliability is essential, as it allows traders to customize moving averages to their preferences and goals.
Adjusting the Moving Average for Specific Trading Strategies
Moving averages may be modified or combined to meet certain trading strategies. Here are a few illustrations:
- Multiple Moving Averages: Multiple moving averages with different period lengths are widely used by traders to catch both short- and long-term trends at once. It is standard practice to combine a shorter-term moving average (such as 20 days) with a longer-term moving average (such as 50 or 200 days). These moving average crossings may generate trading signals.
- Moving Average Envelopes: To define trading ranges or spot overbought and oversold circumstances, traders might draw bands or envelopes around a moving average. An exact percentage above and below the moving average can be chosen for these envelopes.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): An EMA and another moving average make up this well-known indicator. In addition to creating a signal line from a shorter EMA of the MACD line, it calculates the difference between two moving averages and displays it as a line. The MACD can produce buy and sell signals based on crosses or divergences.
- Moving Average Ribbons: On a similar chart, many moving averages are shown, each with a slightly different period length. This gives the trends a visual representation and makes it easier to spot probable entry or departure locations.
To design a trading system that supports their approach, traders might alter moving averages and incorporate them with other indicators or strategies. Before adopting tweaks or combinations in live trading, it is crucial to fully back-test and validate them to guarantee their efficacy and consistency.
Moving averages are calculated by adding certain price data points over a given period and dividing the result by the total number of periods. The required responsiveness and reliability determine the period. Traders may adjust moving averages to fit their trading methods by using tools like multiple moving averages, envelopes, MACD, or ribbons, among others.
Moving Averages as Trend Indicators
In technical analysis, moving averages are frequently employed to spot patterns in the financial markets. They offer useful information about a trend's intensity and direction. Moving averages reduce price swings and aid traders in making better-informed decisions by estimating the average price for a certain time.
Identifying the direction of a trend is one of the principal applications of moving averages. A simple moving average (SMA) considers the average closing prices over a specific period of time.
Traders can visually determine whether the price is typically trending up or down by charting this average on a price chart.
The slope of the moving average may indicate the trend's strength. The moving average's upward slope indicates a bullish trend, which indicates that prices have been rising steadily. A downhill slope, on the other hand, shows a negative tendency when prices are consistently falling. The tendency is greater the steeper the slope.
Popular methods for spotting potential trend reversals include using the Golden Cross and Death Cross signals.
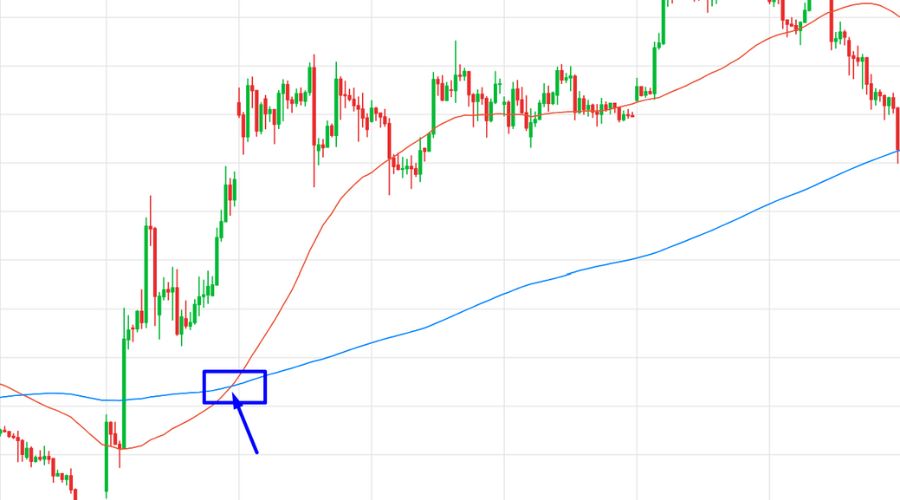
Golden Cross
A "Golden Cross" occurs when a shorter-term moving average, like the 50-day SMA, crosses above a longer-term moving average, like the 200-day SMA. This bullish crossover is seen as a positive indication of a potential shift from a negative trend to a bullish one.
Death Cross
On the other hand, a "Death Cross" happens when a shorter-term moving average crosses below a longer-term moving average. This bearish crossover suggests that the bullish trend may be transitioning to a bearish one.
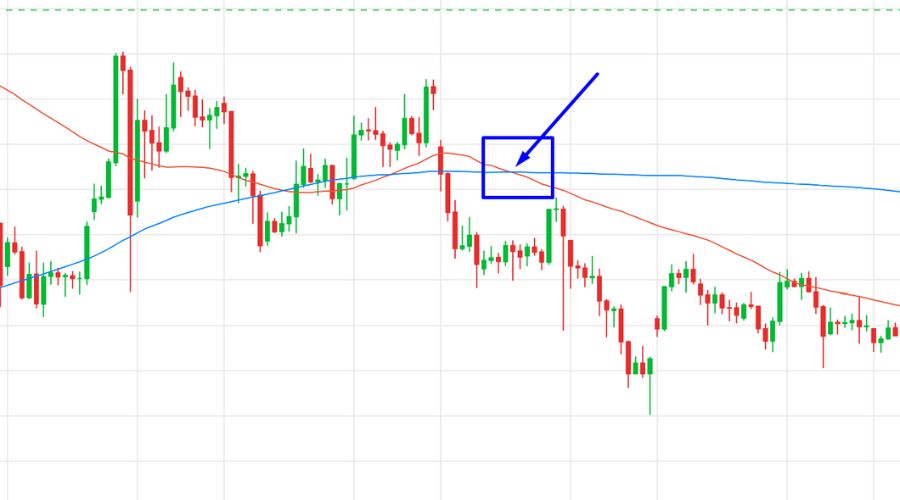
Traders often interpret the signals of the Golden Cross and Death Cross as confirmations of trend reversals, guiding them to take appropriate actions such as entering or exiting positions.
Using Moving Averages as Support and Resistance Levels
Moving averages serve as dynamic levels of support and resistance in technical analysis, providing valuable insights into potential market reversals. Placing a moving average on a price chart creates a line that represents the average price over a specific period. When prices trade above this line, it often acts as a support level, while trading below it signifies a resistance level.
- Support levels indicate prices where in sufficient buying pressure is expected to prevent further price declines. When prices approach or touch the moving average from below and then bounce upward, it confirms the moving average as a support level. Traders often perceive these bounces as potential buying opportunities.
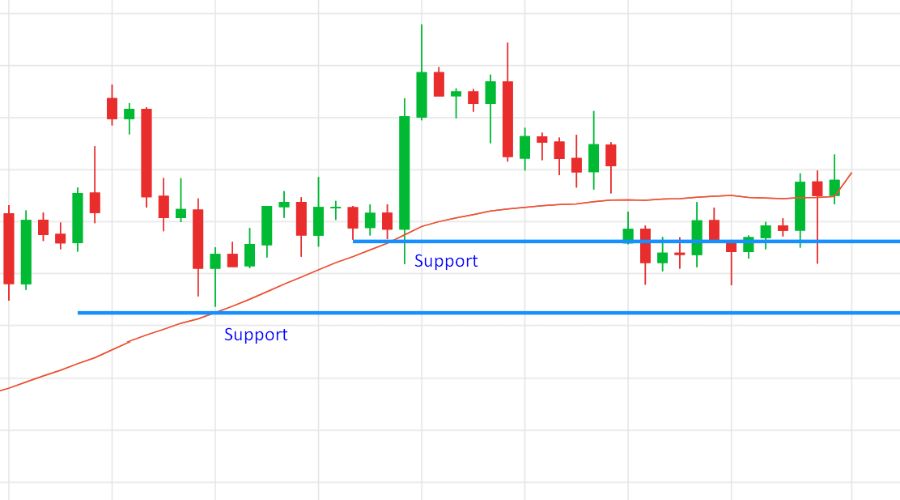
- On the other hand, resistance levels are price levels where selling pressure is anticipated to be strong enough to halt upward price movements. If prices approach or touch the moving average from above and subsequently reverse direction, it indicates that the moving average is acting as a resistance level. Traders may view these situations as potential selling opportunities.
By utilizing moving averages as levels of support and resistance, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve their ability to identify favourable entry and exit points in the market.
Bounces and Breakouts from Moving Averages
Two common price reactions around moving averages are bounces and breakouts. When prices approach or touch a moving average, they often bounce off, continuing in the same direction as the prevailing trend. Traders frequently rely on these bounces to confirm support or resistance levels and guide their trading decisions.
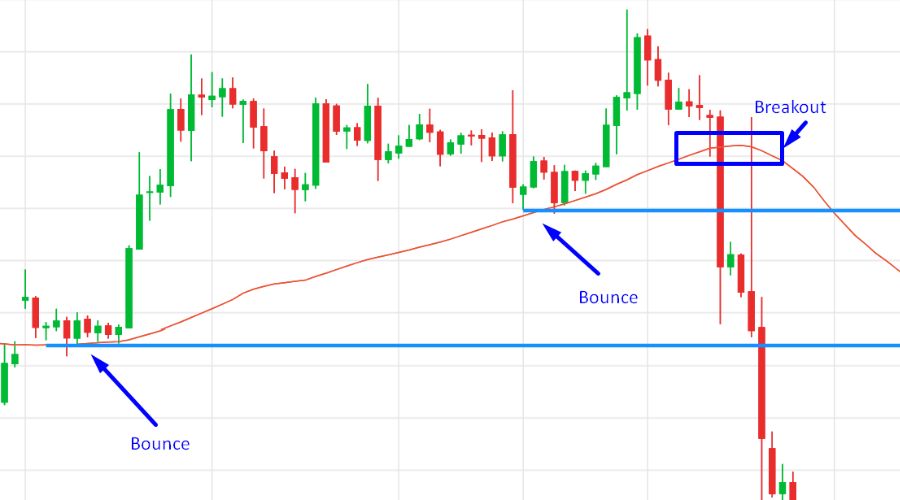
On the other hand, a breakout occurs when prices make a clear and decisive move through a moving average, either breaking above a resistance level or falling below a support level. Breakouts from moving averages can serve as indications for traders to initiate or exit trades, as they may suggest a potential trend reversal or acceleration.
Enhancing Support and Resistance Confirmation with Other Indicators
Traders often combine moving averages with other technical indicators to reinforce the confirmation of support and resistance levels provided by moving averages. For example, they may use trend lines, chart patterns, or oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to validate the relevance of a moving average as a support or resistance level.
By incorporating additional technical indicators, traders can increase the reliability of support and resistance levels derived from moving averages. This comprehensive approach helps eliminate false signals and provides a more robust foundation for making informed trading decisions.
Moving Average Crossovers Strategies
Trading signals are generated through moving average crossovers, a popular method in technical analysis. These techniques involve the intersection of different moving averages and can provide insights into potential trend shifts and entry/exit opportunities. Two well-known moving average crossover strategies are the Simple Moving Average (SMA) crossover and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) crossover.
Simple Moving Average (SMA) Crossover Strategy
The simple moving average (SMA) crossover strategy involves comparing the price movement using two moving averages with different periods, typically a shorter-term and a longer-term average. When the shorter-term moving average crosses above the longer-term moving average, it generates a bullish signal, indicating a potential trend reversal or upward price movement.
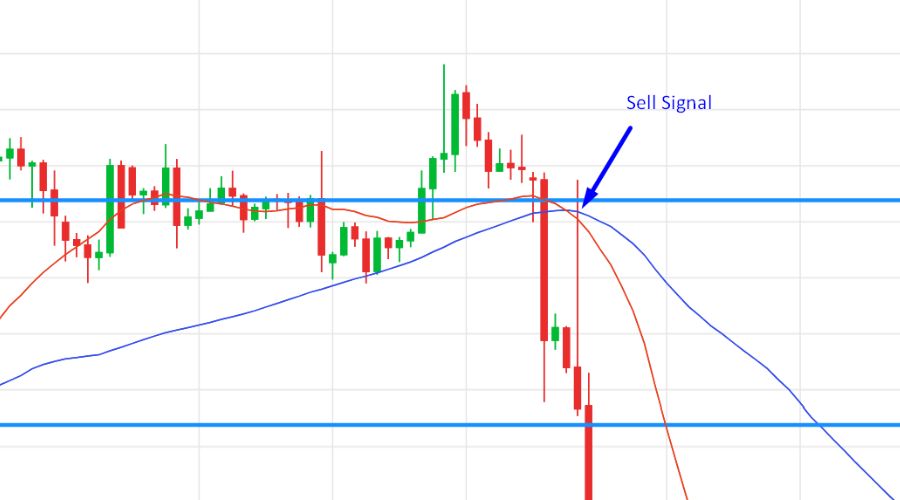
Conversely, a bearish signal is generated when the shorter-term moving average crosses below the longer-term moving average, suggesting a potential trend reversal or downward price movement. Traders often use this strategy to enter or exit positions based on these signals.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) Crossover Strategy
Similar to the SMA crossover approach, the exponential moving average (EMA) crossover strategy places more emphasis on recent price data. The EMA is more sensitive to price movements as it assigns greater weight to the most recent prices than the SMA.
Consequently, the EMA crossover strategy may provide early trading signals. A bullish signal is generated when the shorter-term EMA crosses above the longer-term EMA.
In contrast, a bearish signal is generated when the shorter-term EMA crosses below the longer-term EMA. The interpretation and implementation of the EMA crossover method are similar to the SMA crossover approach.
Pros of Using Moving Average Crossovers:
- Moving average crossover strategies are straightforward and can be easily understood and applied by traders of all experience levels.
- They can be used to identify trends, enabling traders to capitalize on potential market reversals.
- Crossovers provide clear buy or sell signals based on the interaction between moving averages, reducing uncertainty and emotional decision-making.
Cons of Using Moving Average Crossovers:
- Moving averages are lagging indicators as they rely on historical price data, which may result in less precise entry or exit points.
- Crossovers can produce false signals in volatile or choppy market conditions, leading to losses or whipsaws.
- Moving average crossovers are less effective in sideways markets, where they generate more frequent but less reliable signals.
It is important to note that no strategy is foolproof, and traders should complement moving average crossover strategies with other technical analysis tools and risk management techniques.
Comprehensive backtesting and performance analysis are also recommended before implementing the strategy in live trading.
Moving Averages in Combination with Other Indicators
Moving averages can greatly enhance trading strategies and provide traders with a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics when combined with other technical indicators. Three widely used technical indicators that complement moving averages well are Bollinger Bands, the Relative Strength Index (RSI), and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The MACD is a momentum trend-following indicator that assesses the relationship between two moving averages. It consists of three components: the MACD line, the signal line, and the histogram. Traders often use moving averages and the MACD together to generate buy and sell signals. A bullish signal occurs when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, indicating a potential upward price movement.
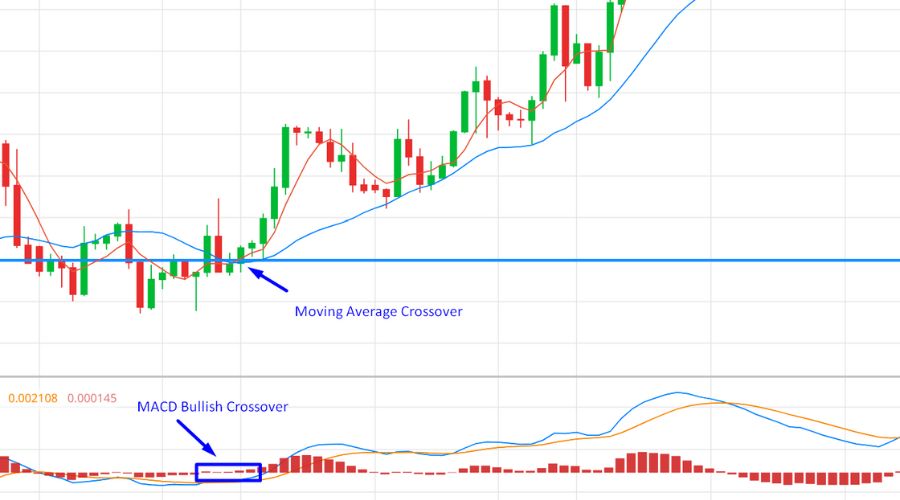
Conversely, a bearish signal occurs when the MACD line crosses below the signal line, suggesting a potential downward price movement. By combining moving averages with the MACD, traders can gain confirmation and deeper insights into trend reversals and market momentum.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI is a popular oscillator that measures the speed and magnitude of price movements. It ranges from 0 to 100 and is commonly used to identify overbought or oversold market conditions. When used with moving averages, the RSI can help traders confirm potential trend reversals.
For example, a possible bearish reversal may be indicated if the price approaches a moving average, and the RSI is in overbought territory (above 70).
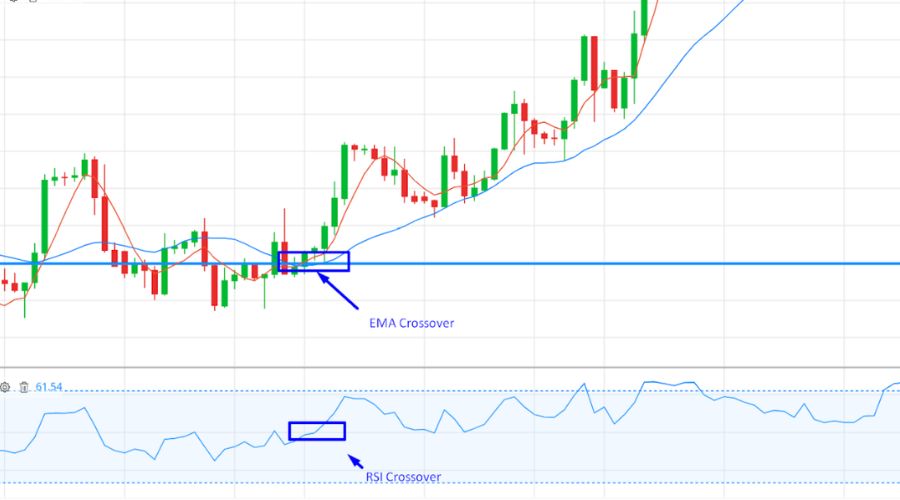
Conversely, a potential bullish reversal may be indicated if the price approaches a moving average, and the RSI is in oversold territory (below 30). By combining moving averages with the RSI, traders can refine their analysis and make better trading decisions.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of an upper band, a lower band, and a middle band (typically a moving average). These bands are constructed based on an analysis of the statistical variance in prices. When the price trades near the upper band, it may indicate a potential reversal or pullback, suggesting that the market is overbought.
Conversely, when the price hovers near the lower band, it may suggest that the market is oversold and could see a bounce or reversal.
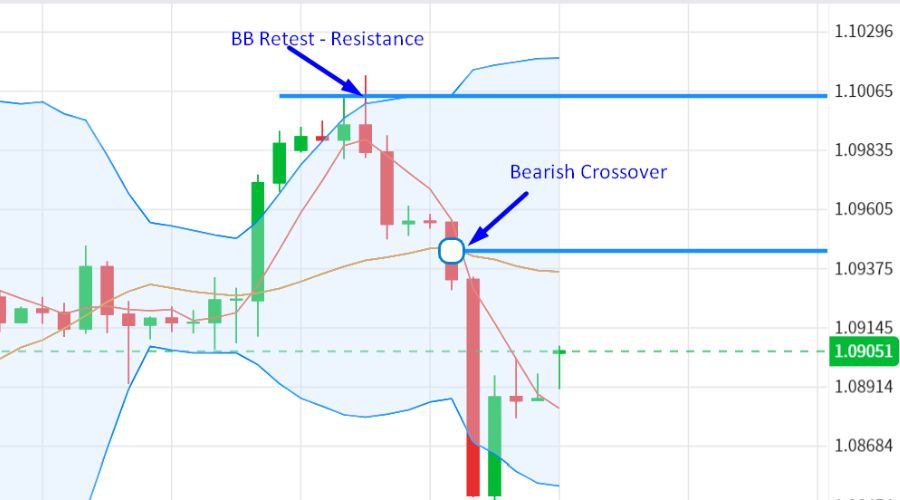
By incorporating Bollinger Bands with moving averages, traders can gain a better understanding of market volatility and trend strength and potentially identify price extremes.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in Using Moving Averages
While moving averages are valuable tools for technical analysis, traders often make mistakes that can negatively impact their trading outcomes. It is important to avoid the following errors when using moving averages:
- Overreliance on Moving Averages: Relying solely on moving averages without considering other indicators or market conditions is a common mistake. While moving averages provide useful information, they should be used with other tools to understand the market comprehensively. Using multiple indicators and conducting thorough research is crucial before making trading decisions.
- Ignoring the Importance of Market Context: Moving averages should always be analysed within the overall market context. Ignoring market volatility, news events, or fundamental considerations can misinterpret moving average signals. It is essential to consider the broader market background alongside moving averages and keep the bigger picture in mind.
- Using Inappropriate Period Lengths for Moving Averages: The chosen period lengths for moving averages can significantly impact their effectiveness. Using extremely short-term moving averages may result in excessive noise and misleading signals, while long-term moving averages may cause slow responses to price movements. Traders should select period lengths that align with their trading strategies, timeframes, and the characteristics of the asset being analysed.
- Failure to Adjust to Changing Market Conditions: Market conditions change over time, and trends may shift or lose validity. Traders sometimes must avoid rigidly sticking to a particular moving average approach without adapting to evolving market conditions. It is essential to regularly review and adjust the setting of moving averages or explore alternative approaches to align with market dynamics.
By avoiding these mistakes and adopting a thoughtful approach to using moving averages, traders can maximize the benefits of these indicators and improve their trading decisions.
Conclusion
Moving averages are powerful technical analysis tools that allow traders to identify trends, determine support and resistance levels, and generate trading signals. These indicators can be enhanced by combining them with other technical indicators such as MACD, RSI, and Bollinger Bands, providing additional confirmation and improving trading strategies.
In conclusion, incorporating moving averages into forex trading techniques can significantly enhance decision-making and trading outcomes. Traders should familiarize themselves with the fundamental concepts behind moving averages, avoid common mistakes, and engage in thorough analysis. To navigate volatile markets successfully, it is advisable to combine moving averages with other indicators, consider the market environment, and adapt strategies as needed. By utilizing moving averages effectively, traders can gain valuable insights and make more informed trading decisions.
Try These Next











