Mastering the Relative Strength Index (RSI): Comprehensive Guide
2023-07-06 15:15:52
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a widely recognised technical oscillating indicator that evaluates market strength and identifies trends through signals. Unlike traditional methods that compare the strength of a forex pair to the broader market, the RSI assesses it relative to its price history. By offering overbought and oversold signals, the RSI assists traders in identifying optimal entry and exit points.
In this comprehensive guide, we aim to provide traders with a deep understanding of the RSI, including its calculation, interpretation, and practical application in forex trading. This guide equips traders with the necessary tools and insights to utilise the RSI and enhance their trading strategies effectively.
Who Created the Relative Strength Index (RSI)?
J. Welles Wilder Jr., a well-known figure in the field of technical analysis, created RSI. In addition to being a real estate developer, he was also a mechanical engineer. His groundbreaking work on the RSI indicator propelled him to greater recognition and popularity within the industry.
Understanding RSI Calculation
The RSI indicator value is determined using the following formula:
RSI = 100 - 100 / (1 + RS)
In this formula, RS represents the ratio of average gains to average losses over a specific period. The RSI value is expressed as a percentage and ranges between 0 and 100.
What Does RSI Show Us?
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) generates various signals due to its dynamic nature. RSI is used to determine the type of trend and potential trend reversals.
When the RSI rises above 50, it indicates increased market participation and buying pressure, resulting in price increases.
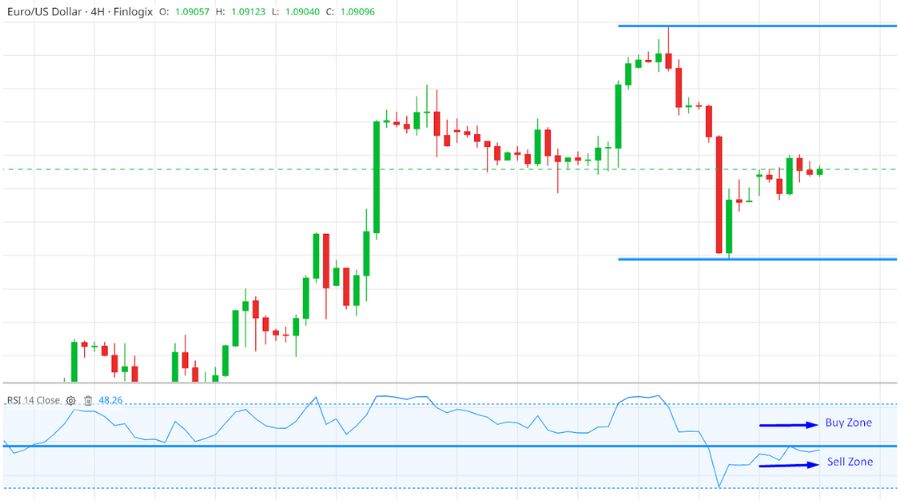
Conversely, when the RSI drops below 50, it suggests more selling pressure than buying, leading to price declines.
Oversold signal
When the RSI indicator value falls below 30, the forex pair is oversold. An oversold signal suggests that the short-term downward movement in the forex market may be reaching its end, potentially setting the stage for a quick rebound.
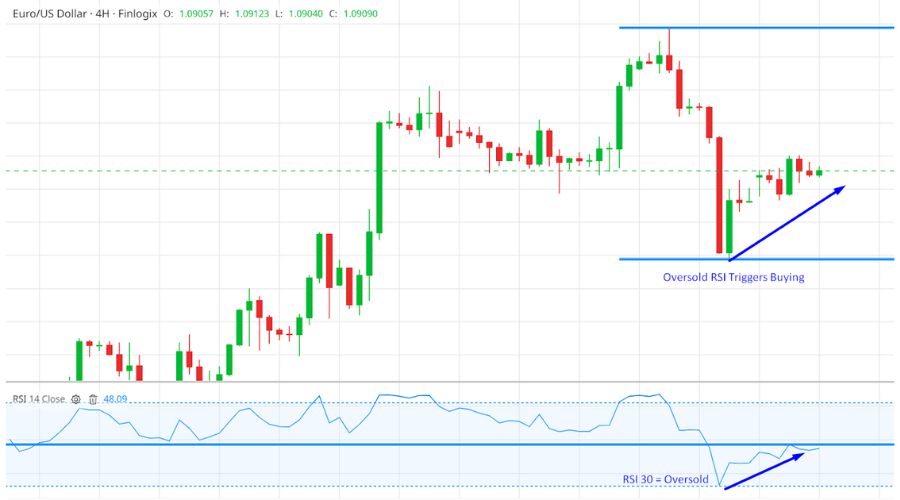
The oversold level indicates a scarcity of sellers in the market, and further downward price movement may be limited.
Overbought Signal
The overbought condition indicates a high likelihood of insufficient buyers in the market to sustain upward momentum in the forex pair, potentially leading to a reduction in price movement.
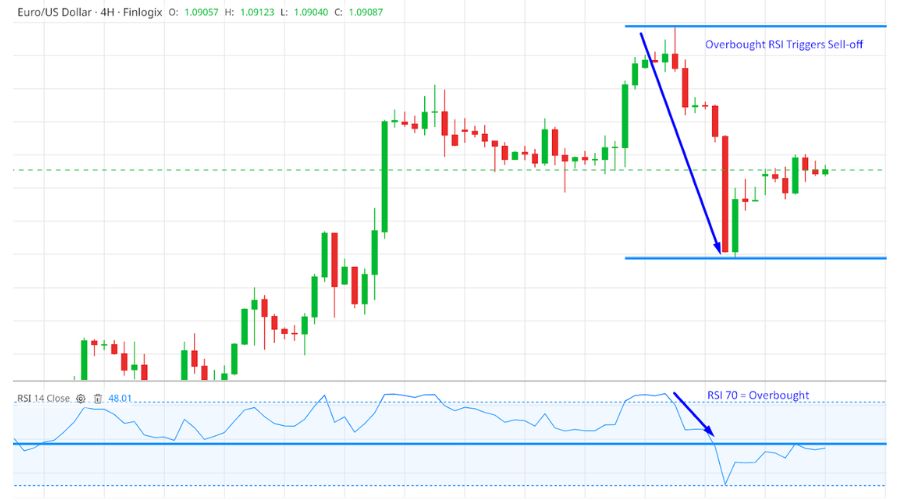
If the RSI exceeds or equals 70, it signifies the start of the overbought region, indicating that the price movement is likely to slow down and possibly reverse downward.
Such a situation is depicted in the screenshot above.
Interpreting RSI and Understanding RSI Ranges
A trader who does not have any open positions can consider utilising the oversold signal as an indication to initiate a new long position, entering the market with a buy order based on the belief that the price will soon experience an upward movement.
Similarly, if a trader has no open positions, they may consider taking the overbought signal as an opportunity to initiate a new short trade. However, if a trader is already in a long position, they may consider utilising the overbought signal to secure profits and close their existing positions.
When trading long, the trader anticipates an increase in the underlying market and aims to close their position by selling.
RSI Divergence
RSI divergence occurs when the price movement of a forex pair differs from the movement of the RSI indicator. It refers to the opposite movement from the expected criteria. Specifically, when the market price highs or lows move in a different direction than the highs or lows on the RSI indicator, it is considered RSI divergence.
Bullish Divergence
A positive or bullish divergence suggests an impending increase in the price of the forex pair within a short time frame. By comparing the lows of the indicator and the price, we can determine the presence of bullish divergence. This occurs when the price forms higher lows while the indicator forms lower lows.
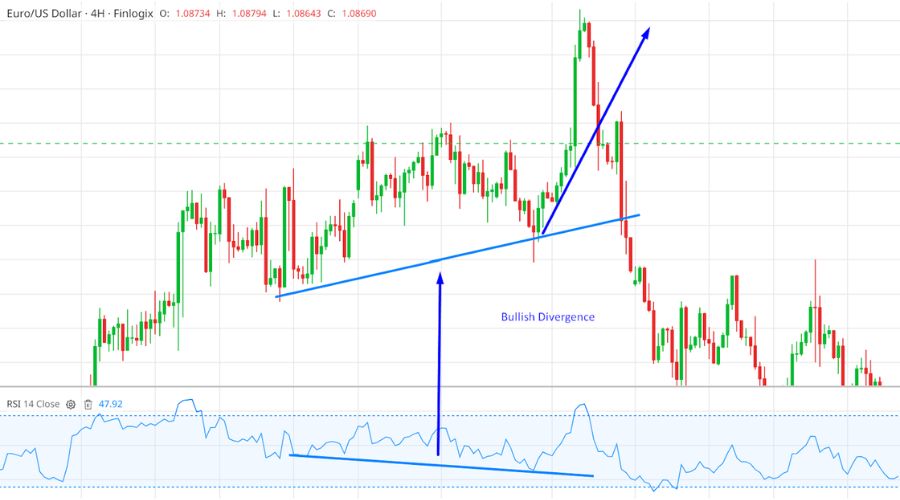
Bullish divergence is more likely to occur when the forex pair is oversold. Market professionals often view a positive divergence signal in combination with an oversold signal as a stronger indication to buy compared to an oversold signal alone.
Bearish Divergence
A short-term decrease in the price of the underlying security is predicted following a negative or bearish divergence. Market professionals consider a negative divergence signal in combination with an overbought signal as a stronger "sell" signal compared to an overbought signal alone.
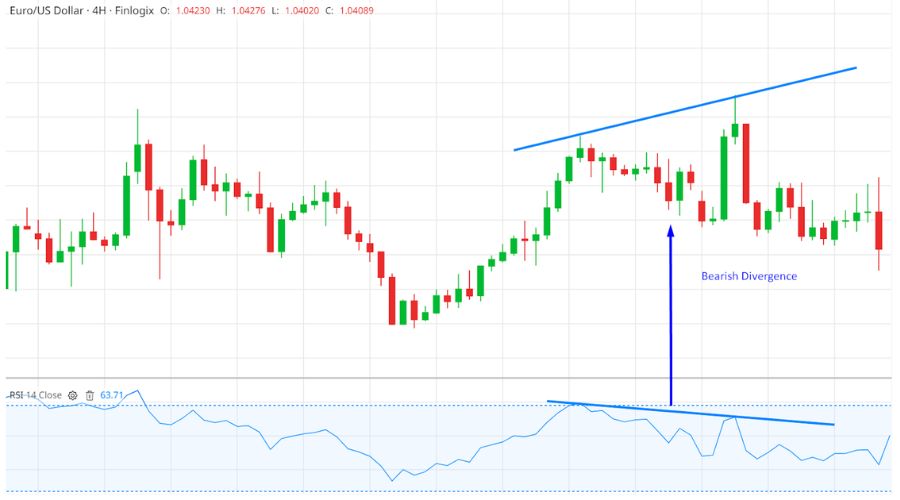
A negative divergence occurs when the price forms higher highs while the indicator forms lower highs. By examining the highs of both the price and the indicator, we can identify a bearish divergence.
Failure Swings
A Relative Strength Index (RSI) divergence occurs when the price and the indicator move in opposite directions, indicating a loss of momentum in the trend. Similarly, breaking the indicator's fail point indicates a movement change in an RSI failure swing. Traders can watch for failure swings on the charts to enter more validated trades.
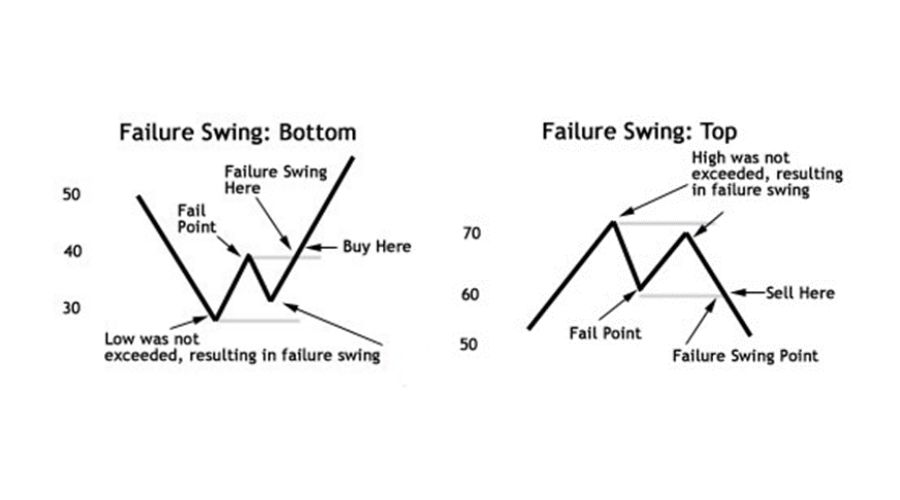
A failure swing top occurs when the price reaches a higher high, but the RSI fails to do so and drops below the indicator's most recent swing low (fail point), triggering a sell signal.
Conversely, a failure swing bottom occurs when the price reaches a lower low, but the RSI fails to do so and rises above the indicator's most recent swing high, signalling a buy signal.
Using RSI in Forex Trading: A Practical Guide
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a powerful tool that can enhance your trading strategy and increase your winning rate in the forex market. By understanding how to use the RSI indicator effectively, you can make better-informed decisions on when to buy or sell.
To gauge the market trend, set the RSI value to a longer period, such as the 200-period. When the 200-period RSI is above 50, the market is likely in an uptrend, suggesting potential buying opportunities. Conversely, when the 200-period RSI is below 50, it suggests a market downturn, indicating potential selling opportunities.
Optimising Entry Timing with the RSI Indicator
The RSI indicator provides valuable insight into market sentiment. When the RSI drops below 30, indicating significant bearish sentiment, it suggests a potential buying opportunity as buying pressure may emerge. Traders can consider entering a forex trade when the RSI rises above 30, signalling the onset of buying pressure.
Capturing Swings for Consistent Profits
Swing trading aims to take advantage of price swings in the forex market. By using a shorter period, such as 20 periods, for the RSI, you can align it with medium-term trades and effectively capture swing opportunities. This allows you to sell during an uptrend as the price rises, maximising profit potential.
By mastering the RSI indicator, you can refine your trading strategy and achieve consistent profits in the forex market. It is important to combine the RSI with other technical indicators and analyses to confirm signals and increase trading accuracy.
Analysing Trends with the RSI Indicator
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a widely used indicator for identifying trend patterns. To determine if a trend is developing, it is recommended to check the RSI and observe if it is above or between 50. If the RSI remains above 50, it suggests a potential uptrend. Conversely, if you are considering a potential downtrend, the RSI value would be below 50.
Trading Strategies with RSI: Maximising Profits with Relative Strength Index
Using RSI and MACD: A Strategy for Enhanced Trading Analysis
The combination of the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD) indicators forms the basis of a powerful trading strategy. This approach utilises both indicators to gain deeper insights into market behaviour and make informed trading decisions. Traders can employ these oscillating indicators as swing-trading tools and leverage one indicator to confirm signals from the other. For instance, when the RSI shows an upward movement after entering the oversold zone and the MACD rises above the signal line, it may signal a potential long trade opportunity.
RSI and Moving Average: A Confluence for Actionable Signals
Another effective approach is to combine the RSI with moving average crossovers. Traders can look for short-term moving average crossovers, such as the 5 EMA crossing over the 10 EMA, in conjunction with RSI indications of overbought conditions and potential trend reversals. When the 5 EMA moves from above to below the 10 EMA, it provides further confirmation of the RSI's signal. Conversely, an upside crossover of the moving averages suggests that the market may have been oversold.
RSI and Bollinger Bands: Spotting Consolidation and Breakout Opportunities
By incorporating Bollinger Bands into the analysis along with RSI, traders can identify market consolidation phases and potential breakout or reversal points. To utilise the RSI with Bollinger Bands, traders should observe instances where the RSI line breaks either the upper or lower Bollinger Bands. A crossover above the upper band indicates a possible overbought condition, suggesting a correction or reversal may occur. Conversely, when the RSI falls below the lower band, it signals an oversold condition and implies a future price rise. Traders can also monitor the width of the Bollinger Bands around the RSI, as wide bands indicate high volatility while narrow bands indicate low volatility.
RSI and Fibonacci Retracements: Utilising Ratios for Price Analysis
Experienced traders are familiar with Fibonacci retracement ratios, which help identify potential reversal points and levels of support and resistance. By combining the RSI with Fibonacci ratios, traders can validate price movements. The RSI can provide insights into whether a Fibonacci ratio is influencing price action, further supporting trading decisions.
With these strategies combining RSI with MACD, moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci retracement, traders can enhance their analysis and increase the accuracy of their trading signals, leading to improved trading outcomes.
Drawbacks of RSI: Limitations to Consider
Traders need to be aware of certain drawbacks associated with the Relative Strength Index (RSI). One notable weakness is its tendency to remain in overbought or oversold territory for prolonged periods. Since the RSI is designed to detect price reversals, it inherently operates as a counter-trend tool. Buying when the RSI crosses above 30 or when the market is considered "oversold" and selling when the RSI dips below 70 indicates that the market has reached an "overbought" state. However, in extended periods without a distinct trend, the RSI may lack informative value and convey false signals. Therefore, when a market exhibits a strong trend, the RSI's effectiveness diminishes.
Another factor to consider is the impact of market fluctuations on RSI-based trading decisions. While the RSI can be a favourable indicator for entering a range-bound market, it may lead to unfavourable outcomes when the market continues moving in the current direction, placing traders with open positions in a vulnerable position.
RSI vs. Stochastic: Differentiating Momentum Oscillators
In technical analysis, both the RSI and stochastic are price momentum oscillators used to determine market trends. While they share similarities in evaluating market behaviour, each indicator has its own distinct mathematical formulation. Traders often gravitate toward the Relative Strength Index, but the importance of both indicators should be considered.
The RSI calculates price movements by identifying overbought and oversold levels based on the average gain versus average loss over specific periods. On the other hand, the stochastic indicator reflects the closing price relative to the highest high and lowest low over a specified time frame. The stochastic consider overbought and oversold signals at levels 80 and 20, while the RSI identifies these readings at levels 70 and 30, respectively.
To make well-informed trading decisions, traders should incorporate both indicators in their analysis and wait for signals to align, providing additional confirmation before taking action. By utilising both the RSI and stochastic, traders can gain a more comprehensive understanding of market momentum and enhance the accuracy of their trading strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relative strength index (RSI) is a valuable tool for forex traders to assess overbought and oversold conditions in the market. By identifying potential reversals and market extremes, traders can develop intraday trading strategies to capitalise on RSI signals. However, it is important to note that RSI works best when used with other technical indicators and analysis techniques. Combining RSI with indicators such as MACD, moving averages, Bollinger Bands, or Fibonacci retracement can provide a more comprehensive view of market trends and enhance trading decisions.
At ACY Securities, we are committed to providing educational resources and tools to empower traders. Our comprehensive guides, articles, and trading tutorials equip traders with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively use technical indicators like RSI in their forex trading strategies. Whether you are a novice or an experienced trader, our educational materials can help you enhance your understanding of RSI and improve your trading outcomes.
Take the next step in your trading journey with ACY Securities. Visit our website to access our educational materials and explore the wide range of trading services and tools we offer. Start harnessing the power of RSI and other technical indicators to elevate your forex trading success.
Sign up with ACY Securities and enhance your trading knowledge today.
Try These Next











